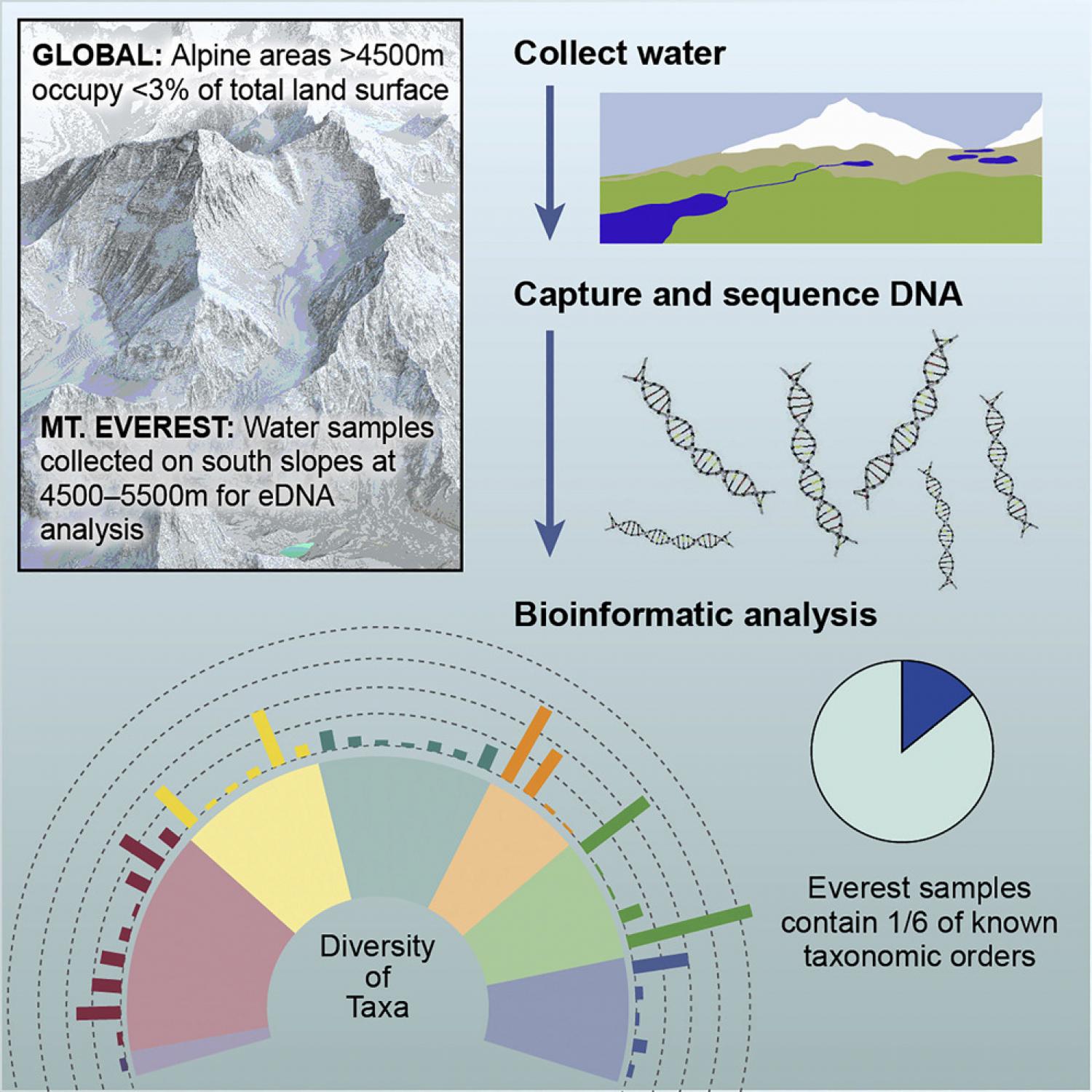
Species composition in high-alpine ecosystems is a useful indicator for monitoring climatic and environmental changes at the upper limits of habitable environments. We used environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis to document the breadth of high-alpine biodiversity present on Earth's highest mountain, Mt. Everest (8,849 m a.s.l.) in Nepal's Khumbu region. In April-May 2019, we collected eDNA from ten ponds and streams between 4,500 m and 5,500 m. Using multiple sequencing and bioinformatic approaches, we identified taxa from 36 phyla and 187 potential orders across the Tree of Life in Mt. Everest's high-alpine and aeolian ecosystem. These organisms, all recorded above 4,500 m—an elevational belt comprising <3% of Earth's land surface—represents ∼16% of global taxonomic order estimates. Our eDNA inventory will aid future high-Himalayan biomonitoring and retrospective molecular studies to assess changes over time as climate-driven warming, glacial melt, and anthropogenic influences reshape this rapidly transforming world-renowned ecosystem.
