Objective
To identify the factors most closely related to hesitancy to influenza vaccination in healthcare workers.
Material and methods
Cross-sectional descriptive study using a quantitative online survey in healthcare workers nationwide, stratifying by workplace and professional profile and using the most appropriate distribution channels at the regional level. The fieldwork took place from 17 February to 31 March 2020.
Results
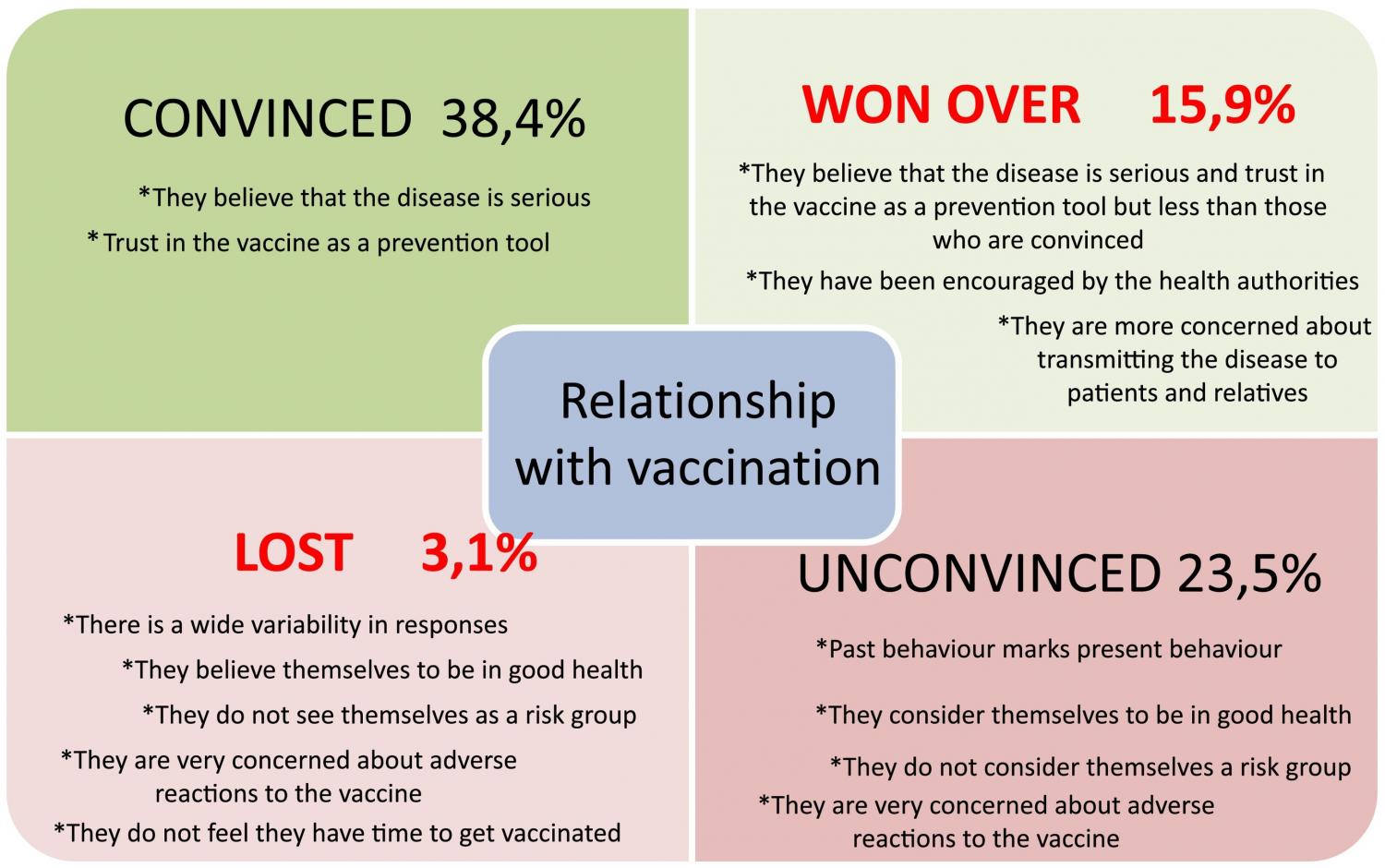
11 108 surveys were collected. There is good knowledge about influenza vaccination in healthcare workers (percentages higher than 85%), being less in nursery and other healthcare workers. Younger personnel have a lower perception of risk and less vaccination, they recognise their role as receptors but less as transmission agents (statistical significance). The recommendation is heterogeneous between the different target groups in all healthcare workers. Information campaigns with common messages are highly demanded. Previous vaccinations joined to training/teaching in vaccines are the most closely reasons related with current vaccination or recommendation to vaccinate.
Conclusions
Confidence in the recommendation of healthcare workers is the main factor that leading to vaccination against influenza in the population. It is necessary to develop comprehensive, educational, and informative, participatory strategies, aimed at the target population and incorporating the identified distinctive results, which are able to improve vaccination coverage in all groups in which influenza vaccination is recommended.
