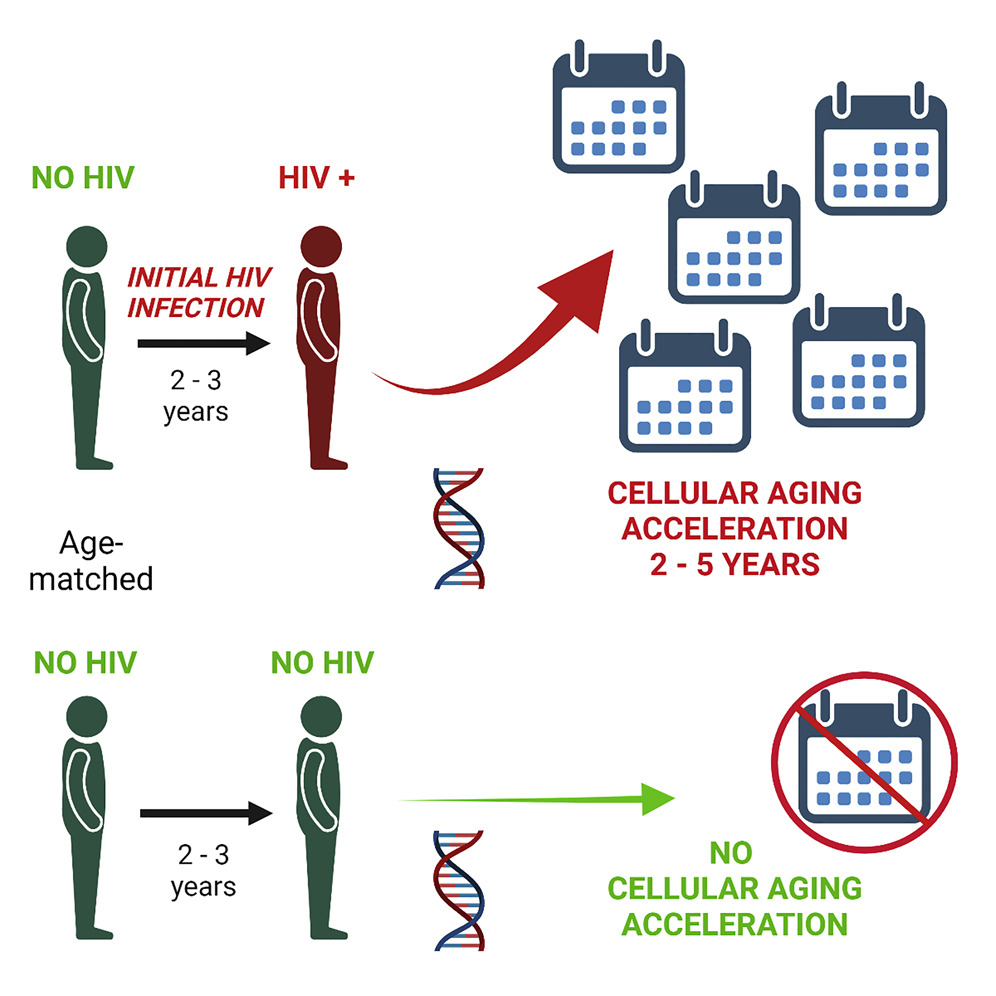
HIV/AIDS remains a significant global health challenge, impacting millions of lives worldwide and intersecting profoundly with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) established by the United Nations. The SDGs aim to address global challenges, including health, poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace, and justice. HIV/AIDS intersects with several of these goals but most directly with SDG 3, which aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. Specifically, target 3.3 of the SDGs seeks to end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, and neglected tropical diseases by 2030, highlighting the integral relationship between HIV/AIDS eradication efforts and global development objectives.
The battle against HIV/AIDS is intrinsically linked to other SDGs beyond health (SDG 3). For instance, SDG 1 aims to eradicate poverty, which is closely tied to the HIV epidemic; individuals in impoverished communities often lack access to necessary healthcare services, including HIV prevention and treatment, making them more susceptible to the virus. Furthermore, SDG 4, which focuses on quality education, plays a critical role in HIV prevention. Educating individuals about HIV transmission, prevention, and stigma can significantly reduce the virus's spread. Additionally, SDG 5 targets gender equality, which is crucial in the fight against HIV/AIDS. Women and girls often face higher risks and barriers to accessing HIV/AIDS treatment due to gender-based inequalities. Addressing these inequalities is essential for effective HIV prevention and treatment strategies.
Moreover, achieving SDG 10, reduced inequalities, is fundamental in combating HIV/AIDS. Marginalized groups, including people living with HIV, often face discrimination and social stigma, hindering their access to healthcare and support services. By promoting inclusivity and reducing inequalities, communities can better support all individuals affected by HIV/AIDS, thereby enhancing public health outcomes and moving closer to eradicating the disease. The interconnectivity of the SDGs underscores the necessity of a holistic approach to global development challenges. Eradicating HIV/AIDS is not only a matter of addressing health disparities but also involves tackling broader societal issues such as poverty, education, gender inequality, and discrimination. The global community's commitment to the SDGs provides a framework for coordinated efforts to combat HIV/AIDS, showcasing the critical intersection of health and development in achieving a more equitable and healthy world.
World AIDS Day
World AIDS Day, observed annually on 1st December, is an opportunity for people around the globe to unite in the fight against HIV/AIDS, support those affected, and remember those who have lost their lives to the disease.