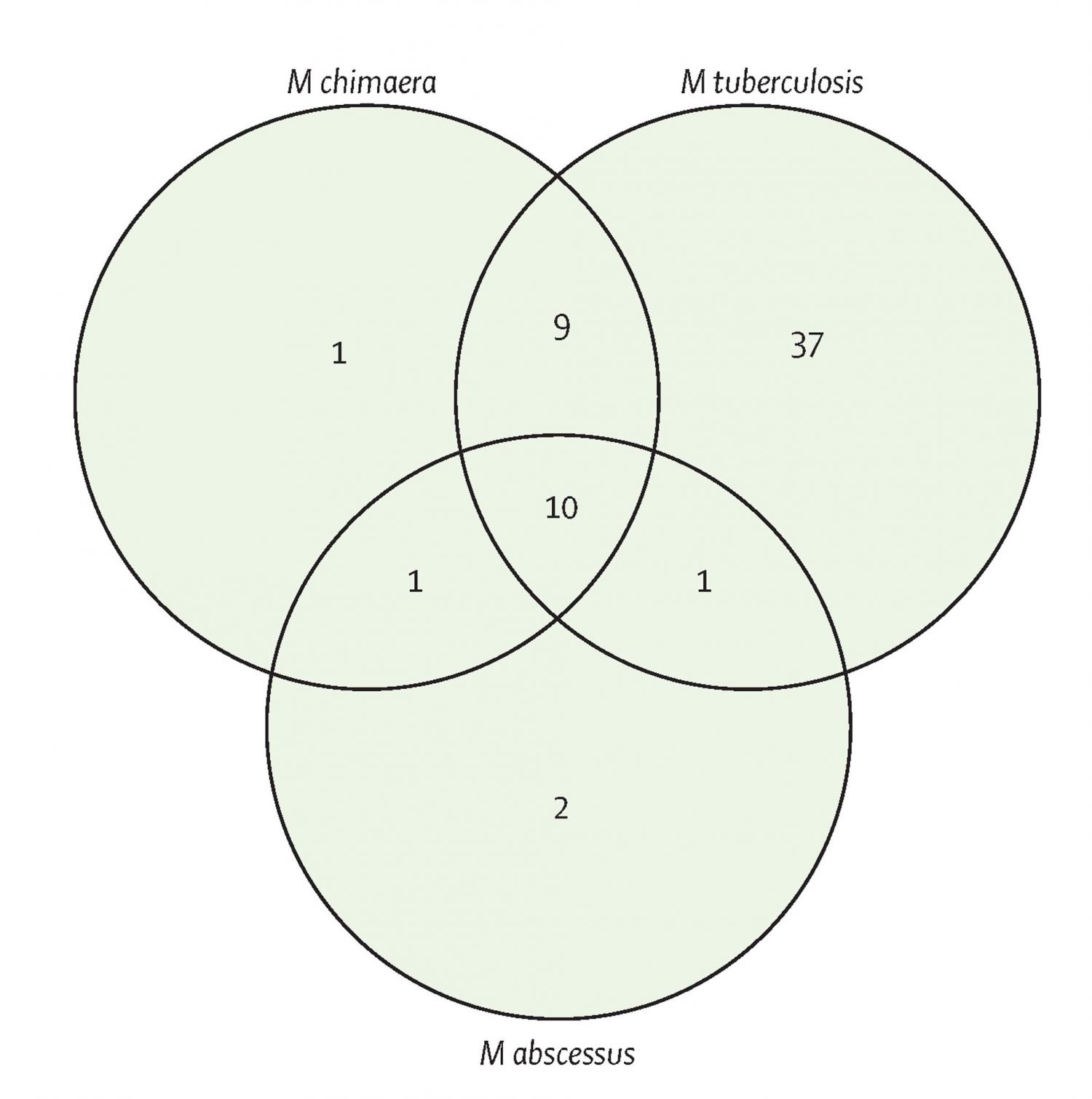
Background: Mycobacterium chimaera is a slowly growing non-tuberculous mycobacterium associated with outbreaks of fatal infections in patients after cardiac surgery, and it is increasingly being detected in patients with chronic lung conditions. M chimaera can cause disseminated disease, osteomyelitis, and chronic skin or soft-tissue infections. We aimed to find new inhibitory compounds and drug repurposing opportunities for M chimaera, as current therapeutic options often result in poor outcomes. Methods: In an open drug discovery approach, we screened the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) Pathogen Box to assess the in-vitro antimicrobial drug susceptibility of M chimaera compared with the antimicrobial drug susceptibility of the slowly growing, major human pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and the rapidly growing Mycobacterium abscessus reference strains. Compounds identified from an initial resazurin microtitre cell viability assay screen were further characterised by determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of MMV Pathogen Box compounds against M chimaera; and the MICs of a panel of 20 drugs commonly used to treat mycobacterial infections against M tuberculosis, M abscessus, and M chimaera. We also assessed the time-kill kinetics of doxycycline, clarithromycin, ethambutol, and rifabutin against M chimaera. Findings: M chimaera was inhibited by 21 (5%) of 400 compounds in the Pathogen Box. Ten compounds were active against all three mycobacteria. MMV675968, with activity against slowly growing mycobacteria that probably targets folate metabolism, had a mean MIC of 2·22 μM (0·80 μg/mL) against M chimaera. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed that oxazolidinones such as linezolid (mean MIC 3·13 μg/mL) were active against M chimaera and that bedaquiline was the most potent compound (mean MIC 0·02 μg/mL). Doxycycline, a broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug with excellent tissue penetration properties, also inhibited M chimaera with a mean MIC of 6·25 μg/mL. Interpretation: Molecular diagnostics present an opportunity for more effective, targeted drug therapies—treating bacterial infections at the species level. Using an open drug discovery platform, we identified compounds that inhibit the newly recognised pathogen M chimaera. The existing evidence base is poor and the option for expensive drug discovery is improbable; therefore, we have also found options for drug repurposing. Future in-vivo efficacy studies will reveal whether these findings result in new, targeted treatment regimens for M chimaera. Funding: Wellcome Trust, National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research (NC3Rs), and the University of Sussex Junior Research Associate scheme.
