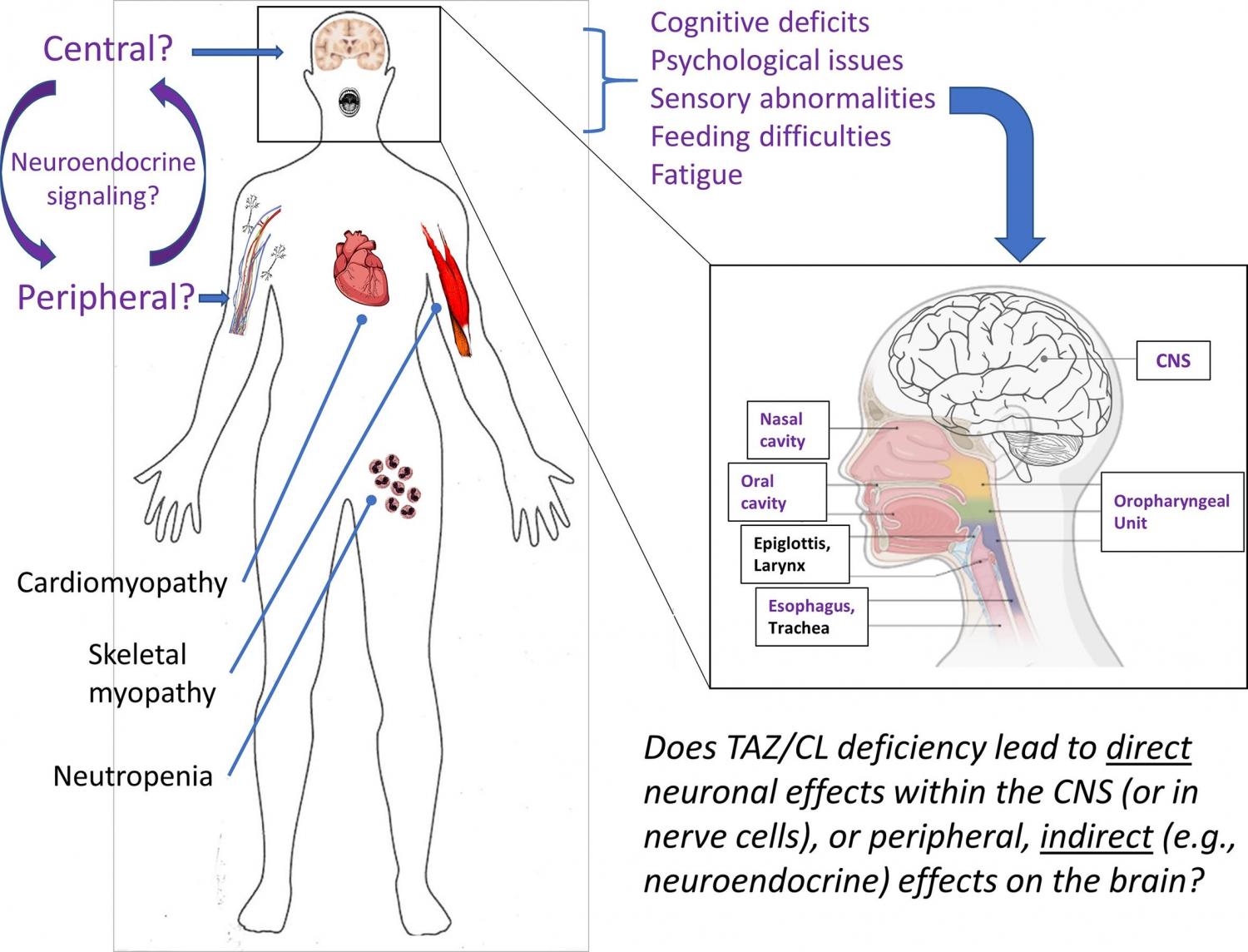
Barth syndrome is a rare X-linked multisystem mitochondrial disease that is caused by variants in the tafazzin gene leading to deficient and abnormal cardiolipin. Previous research has focused on the cardiomyopathy and neutropenia in individuals with Barth syndrome, yet just as common are the least explored neurological aspects of Barth syndrome. This review focuses on the major neuropsychological and neurophysiological phenotypes that affect the quality of life of individuals with Barth syndrome, including difficulties in sensory perception and feeding, fatigue, and cognitive and psychological challenges. We propose selected pathogenetic mechanisms underlying these phenotypes and draw parallels to other relevant disorders. Finally, avenues for future research are also suggested.
