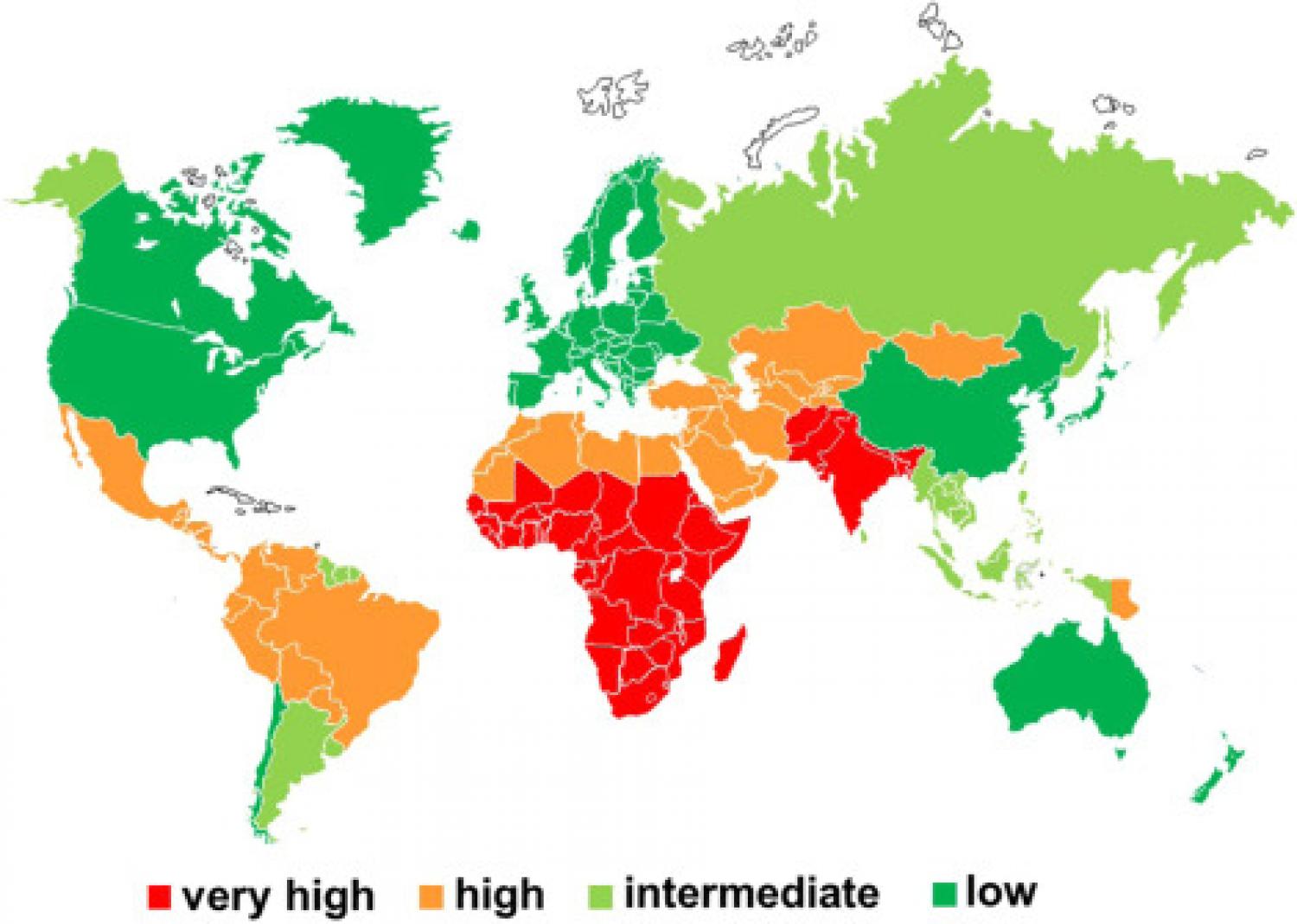
The hepatitis A virus (HAV) and hepatitis E virus (HEV) are the commonest causes of viral hepatitis worldwide. They are enterically transmitted. Several HEV genotypes are zoonotic while others infect only humans. The clinical spectra of HAV and HEV differ, but both acute infections are managed with general supportive care. Chronic infections, HEV only, require specific antiviral treatment based on ribavirin. HAV infections are best prevented by ensuring adequate sanitation and active or passive immunization. HEV infections are also prevented by adequate sanitation in developing countries and on good personal hygiene measures in developed countries, especially cooking at-risk food thoroughly.
