Water and sanitation are pivotal elements of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), primarily encapsulated in SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). This goal seeks to ensure the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all by 2030. This objective directly addresses the current global water crisis, where nearly 2.2 billion people live without access to safe water, and about 4.2 billion lack access to adequate sanitation.
By focusing on improving water quality, increasing water-use efficiency, implementing integrated water resources management at all levels, and protecting and restoring water-related ecosystems, SDG 6 addresses not only direct human needs but also the broader ecological health of the planet. Furthermore, efforts towards achieving SDG 6 indirectly promote several other SDGs.
For instance, water and sanitation are crucial to achieving SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), as clean water and proper sanitation facilities reduce the spread of water-borne diseases and significantly lower child and maternal mortality rates. Likewise, they are foundational to SDG 4 (Quality Education), given that the provision of water and sanitation facilities in schools significantly impacts the attendance and performance of students, particularly for girls.
SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) also intersects with water and sanitation, as sustainable and efficient water management is critical for agriculture, which remains the largest global water consumer. The necessity of water for food production and the potential impact of improved water management on crop yields and livestock health makes SDG 6 integral to achieving zero hunger.
SDG 6 contributes to SDG 1 (No Poverty) and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) as well. Access to clean water and sanitation can enhance economic productivity by reducing time spent gathering water, reducing healthcare costs due to water-related diseases, and even creating jobs in water and sanitation services sectors.
In terms of environmental impact, the sustainable management of water resources is essential for SDG 13 (Climate Action), as water is a key factor in managing climate change due to its role in agriculture and energy production.
Global Groundwater. Source, Scarcity, Sustainability, Security, and Solutions, 2021, Pages 503-517
Global Groundwater. Source, Scarcity, Sustainability, Security, and Solutions, 2021, Pages 577-583
Advances in Chemical Pollution, Environmental Management and Protection, Volume 6, 2020, Pages 1-31
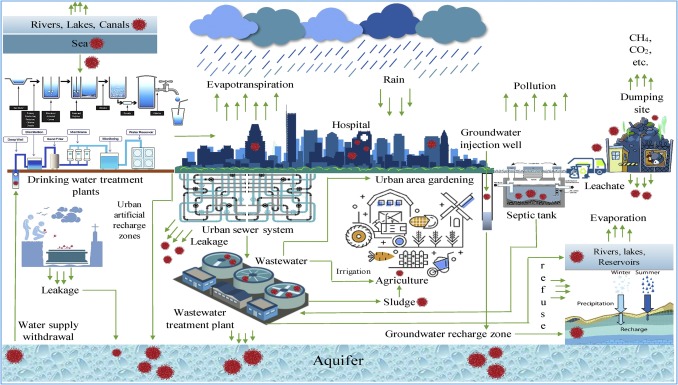
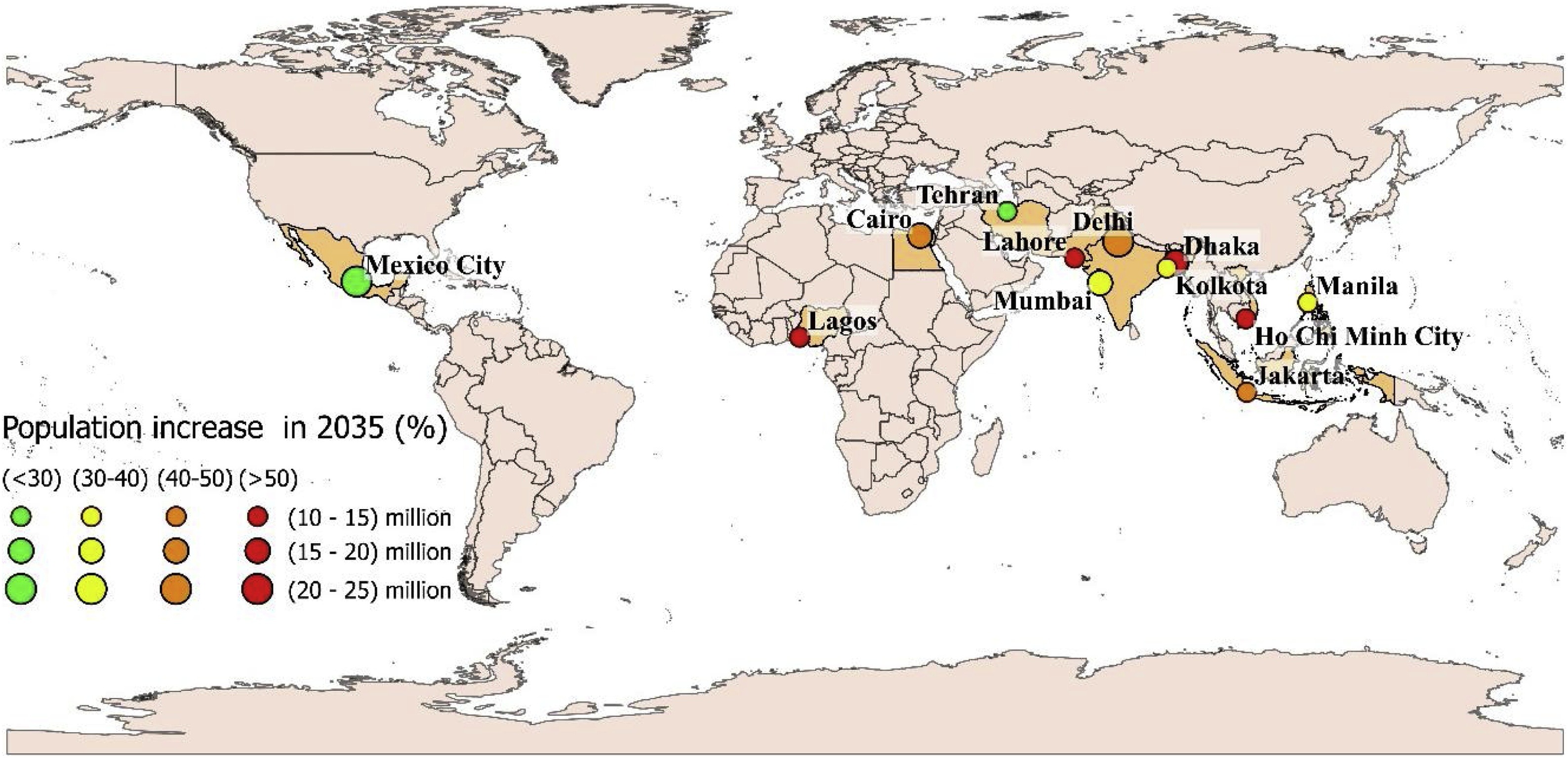
Urbanisation is increasing in many countries, leading to the establishment of 33 megacities, representing huge water demand which is increasingly difficult to supply, exemplified by the recently avoided Day Zero event in Cape Town (2018) and the ongoing water crisis in Chennai, India. The ongoing growth of megacities could lead to the potential for further Day Zero events in countries ill-equipped to deal with such a situation. This study analyses the water supply and demand situations in 12 megacities hosting 194 million people.
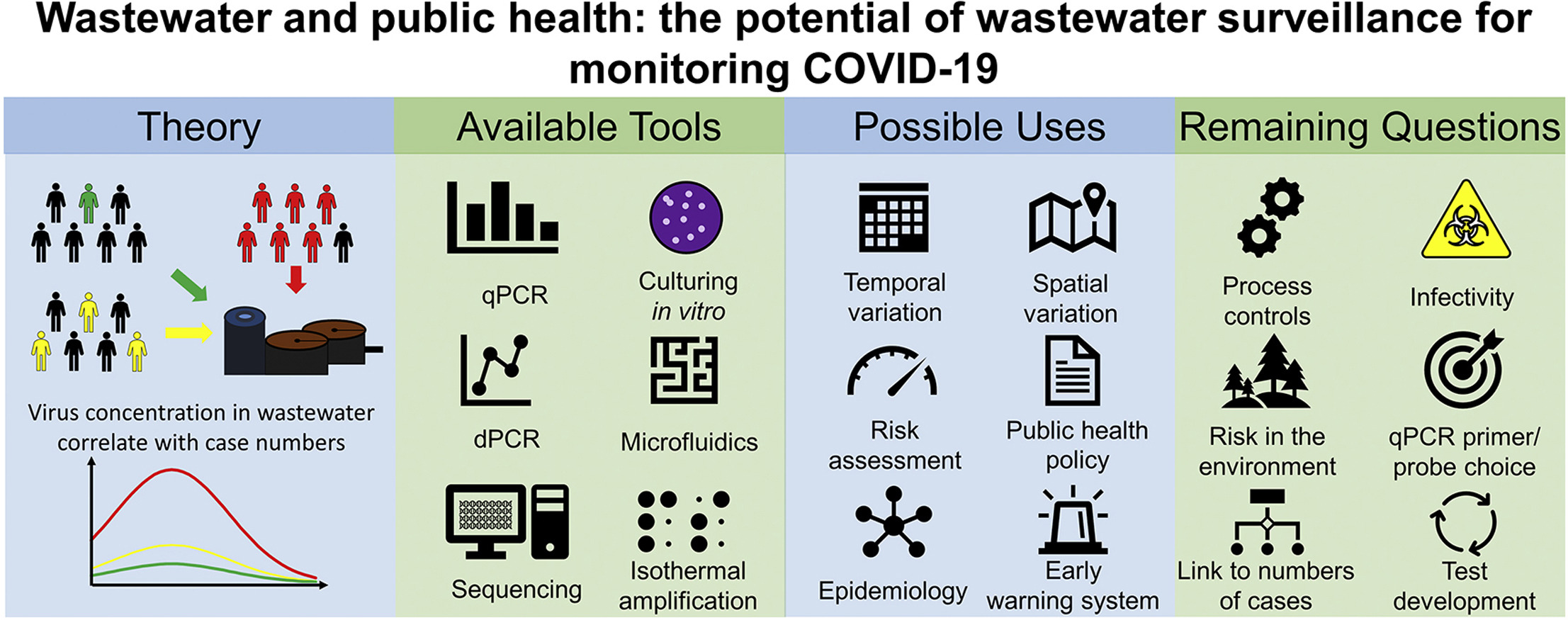
Pathogenic viruses represent one of the greatest threats to human well-being. As evidenced by the COVID-19 global pandemic, however, halting the spread of highly contagious diseases is notoriously difficult. Successful control strategies therefore have to rely on effective surveillance. Here, we describe how monitoring wastewater from urban areas can be used to detect the arrival and subsequent decline of pathogens, such as SARS-CoV-2.