With the growing global environmental awareness, the development of renewable and green materials has gained increased worldwide interest.
A shift to a more healthy and sustainable diet (as recommended by the EAT Lancet Commission report) is currently hampered by persistent choices for meat, which are based on stable preferences and posi
The climate emergency and population growth are challenging water security and sustainable urban design in cities worldwide.
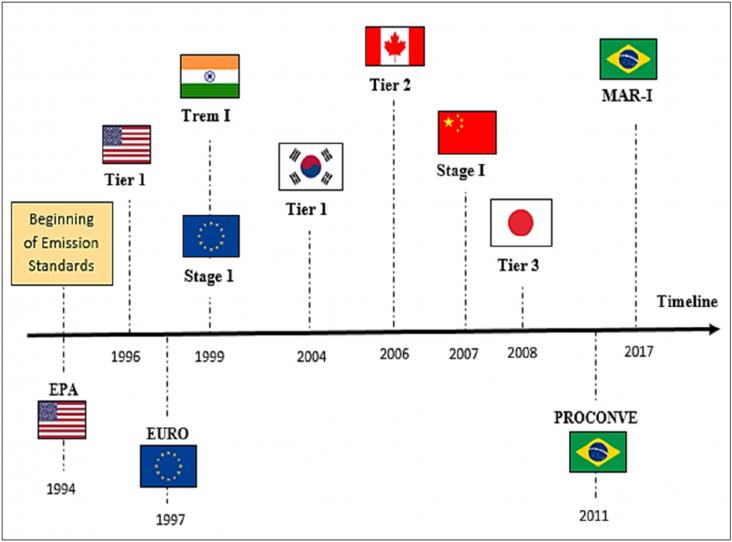
Electric vehicles (EVs) are widely regarded as the key to finally making private mobility clean, yet virtually no research is being conducted on their potential contribution to the expansion of imp
Climate change can have detrimental effects on child health and wellbeing.
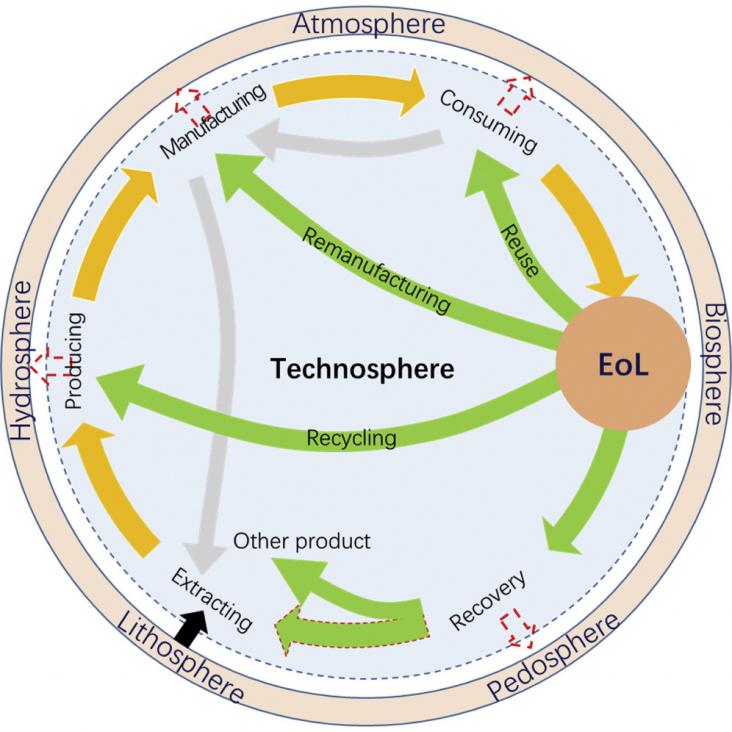
Material depletion over reliance of linear economies and environmental pollution may be resolved by applying the principles and practices of anthropogenic circularity science. Here we systematically review the emergence of anthropogenic circularity science in the interdisciplinary development of green chemistry, supply chain, and industrial ecology at different scales.
This article supports SDGs 7, 9 and 11 by utilizing solar photovoltaic, wind energy, solar thermal energy, and battery energy storage, and the special emphasis is placed on the schedulable value of concentrated solar power generation to provide more economical and environmentally friendly energy supply, while integrating multiple renewable energy technologies through artificial intelligence technology to shape the future of cities.
Background: nationally determined contributions (NDCs) serve to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement of staying “well below 2°C”, which could also yield substantial health co-benefits in the process.
Pollens are a major cause of seasonal allergic diseases. Weather may alter the production of pollens.