The Planetary Health Diet Index (PHDI) is a novel measure adapted to quantify alignment with the dietary evidence presented by the EAT-Lancet Commission on Food, Planet, Health. This review aimed to examine how population-level health and sustainability of diet as measured by the PHDI changed from 2003 to 2018, and to assess how PHDI correlated with inadequacy for nutrients of public health concern (iron, calcium, potassium, and fiber) in the United States. Although there have been positive changes over the past 20 years, there is substantial room for improving the health and sustainability of the United States diet. Shifting diets toward EAT-Lancet recommendations would improve nutrient adequacy for iron, fiber, and potassium. Policy action is needed to support healthier, more sustainable diets in the United States and globally.
Endocrine disruptive chemicals affect negatively women's reproductive systems.
Transitioning to a post-growth economy — i.e., one that doesn't depend on continued economic expansion and resource utilization (SDG 8) — is increasingly seen as necessary to address the climate crisis (SDG 13) and live sustainably within the resource limits of the planet. This One Earth Perspective Article offers policies that could address some of the challenges associated with post-growth economics (i.e., how to avoid recession).
The authors evaluate shifts in water reservoirs (i.e. atmospheric versus terrestrial and underground water storage). Projections indicate water storage deficits in most Southern Hemisphere basins during the summer.
This article links to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by addressing Goal 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), highlighting the urgent need for effective management and reduction of tobacco product waste, which poses significant environmental hazards. By advocating for policies that classify tobacco waste as hazardous and emphasizing the importance of extended producer responsibility, the article underscores the necessity of holding tobacco companies accountable for their environmental impact, thereby contributing to sustainable practices and protecting marine and terrestrial ecosystems.
This study used the SBASInSAR technique to measure long time-series land subsidence in and around Ludhiana city, Punjab, India, and found that the southern, south-eastern, and south-central parts of the study area had been consistently subsiding with an accumulative average land subsidence rate of 24.7 mm/yr during the investigation period from September 2019 to July 2022, while the western and eastern parts were moderately affected, and the northern part experienced slight upliftment.
Food insecurity among Indigenous peoples in Canada is a significant public health issue, impacting all four pillars of food security: availability, access, utilization, and stability. A literature review identified 91 studies indicating that economic disadvantages, high food prices, lack of transportation, and climate change are major contributors to food insecurity. Traditional food systems are disrupted by loss of knowledge, poor food quality, and food safety concerns. Addressing these issues requires culturally specific integrated approaches to improve food availability, cost, knowledge, and quality.
This article ties to SDG3 by examining new methods to assess impact of climate change
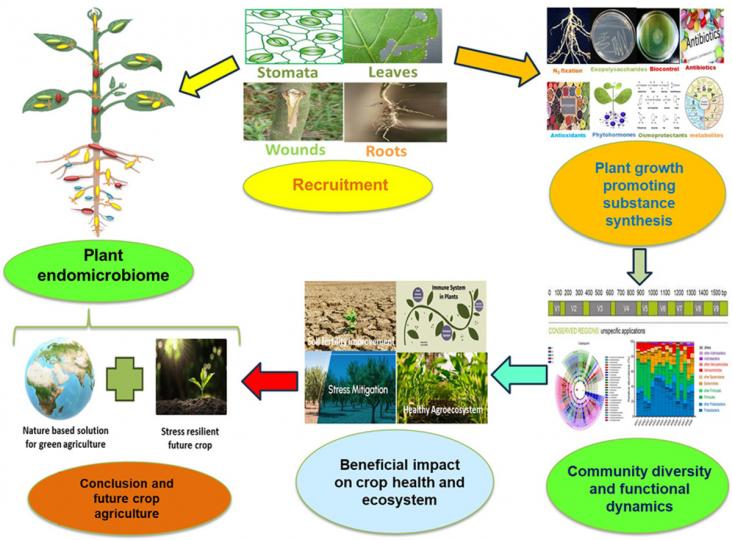
Plants have a microbiome, a diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, living inside and on their tissues. This review article contains deeper insight in endomicrobiome related research work in last years, recruitment, niche development, nutrient dynamics, stress removal mechanisms, bioactive services in plant health development, community architecture and communication, and immunity interplay in producing stress resilient future crop.

Strigolactones (SLs) are a new class of plant hormones that play a significant role in regulating various aspects of plant growth promotion, stress tolerance and influence the rhizospheric microbiome. GR24 is a synthetic SL analog used in scientific research to understand the effects of SL on plants and to act as a plant growth promoter.
