This Review supports SDGs 3, 10, and 15 by examining evidence on Indigenous People's mental health related to resource industries in settler colonial states. It shows that land is central to Indigenous people's mental health, and that land dispossession due to industrial development negatively impacted mental health in Indigenous communities.
First Nations children and adolescents in Australia experience one of the highest reported rates of treatable skin infections in the world, authors of this study gathers information from relevant communities through culturally appropriate, semi-structured interviews, or ‘yarning sessions’. This approach has allowed the authors to centre First Nations voices, identifying strengths and gaps in available resources, services and education to reduce these infections.
This study gives a comprehensive overview of the prevalence, outcomes, treatment, and genetic epidemiology of major depressive disorder within and across the Scandinavian countries.
This population-based cohort study found substantial age-related differences in the proportions of people diagnosed, suggesting an urgent need to improve access to adult autism diagnostic services.
This Article supports SDG 3 by presenting a conceptual framework and a method to estimate cost-effectiveness thresholds for 174 countries, using public and widely available data on country-specific health expenditures and health outcomes; these findings can inform policy makers on the thresholds to consider when deciding on the allocation of health resources.
This Article supports SDG 3 by showing that an HCV testing (point-of-care) and treatment programme implemented in users of a supervised drug cosumption service in Canada was beneficial, with a large degree of positive testing, testing acceptance, and treatment engagement. The study suggests that on-site point of care testing and treatment for HCV in supervised consumption services is effective in reaching this population
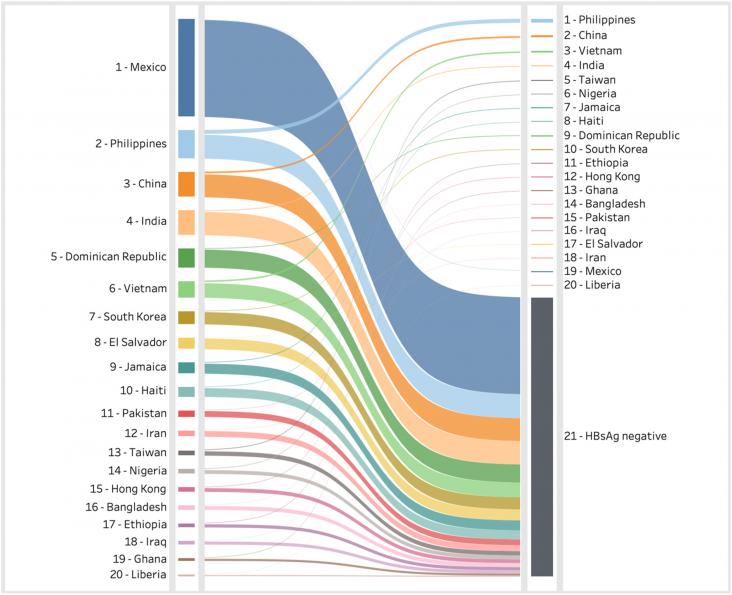
This Article supports SDG 3 by using modelling to estimate the impact of immigration on hepatitis B prevalence in the USA, in order to more accurately assess the hepatitis B burden, which might not be accurately measured by national serosurveys. The study found a significantly higher burden of hepatitis B (1.8 million cases), significantly higher than that found in national serosurveys.
This Article supports SDG 3 by assessing the incidence of HIV and HCV infection among people who inject drugs, a population at higher risk of these infections. In this systematic review, HCV estimates came from studies in 24 countries. Pooled HCV incidence was 12.1 per 100 person-years; data for both infections were scarce, suggesting increased efforts are needed to keep track of these infections in this population.
This Article supports SDG 3 by estimating the burden of low back pain, which continues to be the leading cause of disability worldwide. The study predicts that low back pain prevalence will continue to increase, from 619 million people in 2020 to 843 million in 2050. Two-fifths of the burden are due to modifiable risk factors, and a quarter of years lived with disability are attributable to occupational ergonomic factors.
This paper concludes that findings suggest that 1) long-term omega-3 fatty acid supplementation may reduce risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD); 2) dietary omega-3 fatty acid intake, especially DHA, may lower risk of dementia or cognitive decline; and 3) peripheral biomarkers of omega-3 fatty acids may serve as predictors of cognitive decline. However, further investigation is needed to understand the gene–environment interactions involved in the intake of omega-3 fatty acids.
