
2026's World Leprosy Day: A Unified Call for Dignity and Healing
Celebration and Recognition
The article discusses the potential relationship between alcohol consumptiond the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD), highlighting the role of the serotonergic system as a potential mediator. It synthesizes data from preclinical, clinical, and epidemiological studies to explore how alcohol-induced changes in serotonin function, neuroinflammation, and proteostasis may contribute to the onset and progression of AD
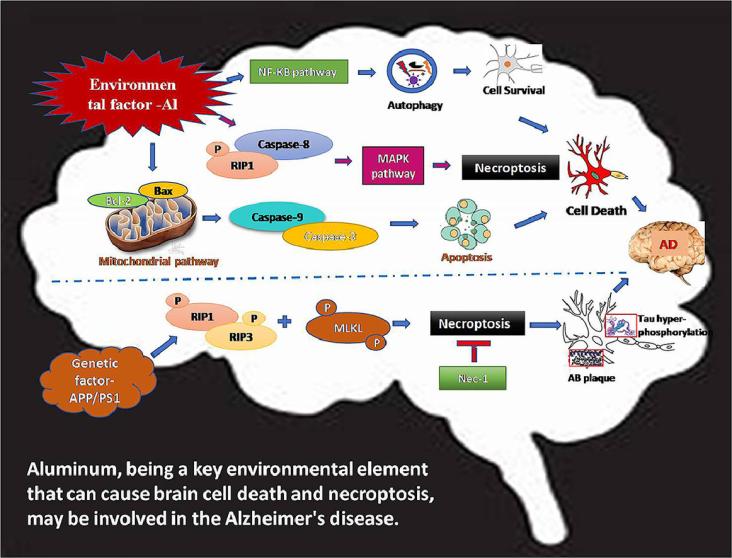
The present article reviews the role of necroptosis, as a novel cell death pathway, in Aluminium-induced Alzheimer’s disease models in vitro and in vivo.
