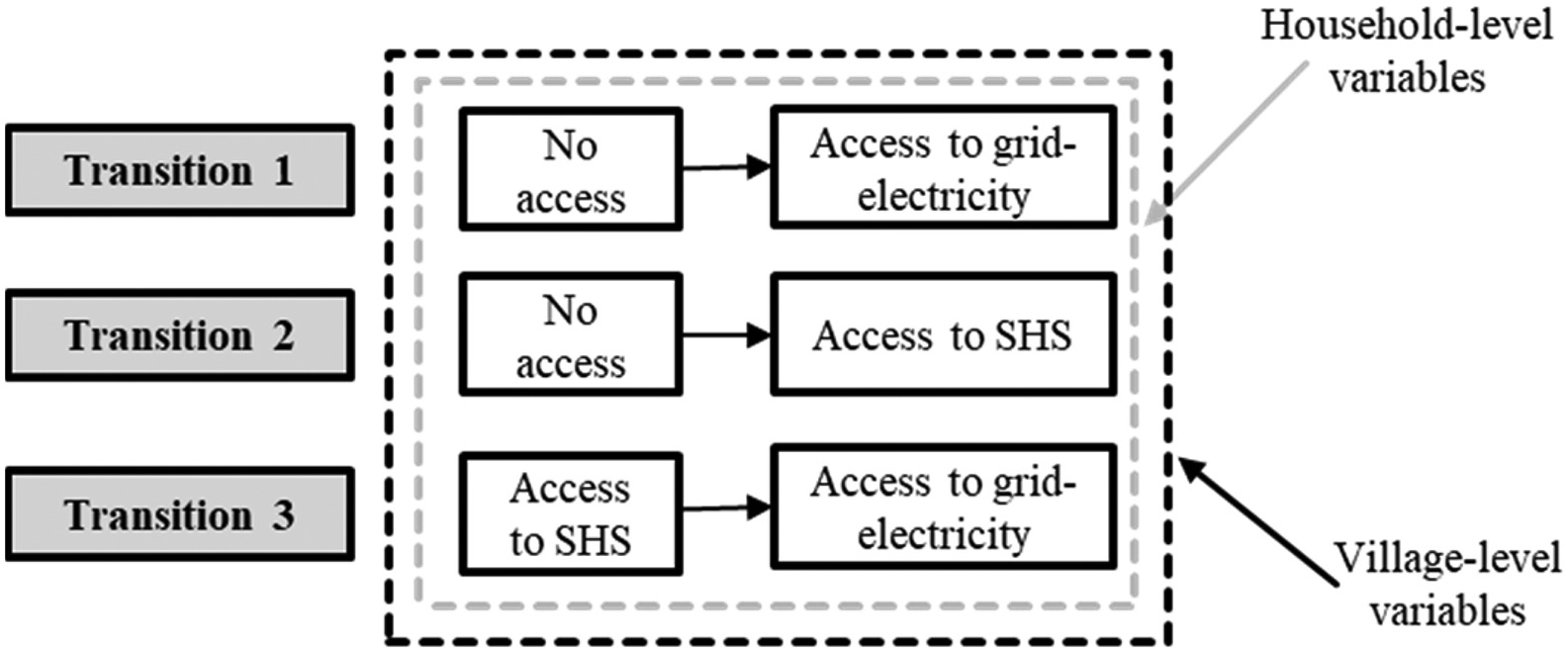
This paper presents an analysis of the path towards a clean energy transition in rural areas, from the time that households do not have electricity access from any source, to when they get access to the national electricity; considering the intermediate access to an off-grid renewable technology, as well as the post-electrification years. For this, field household-level data are collected through surveys and electricity consumption measurements in rural Kenya.
Data-driven digital health technologies have the power to transform health care. If these tools could be sustainably delivered at scale, they might have the potential to provide everyone, everywhere, with equitable access to expert-level care, narrowing the global health and wellbeing gap. Conversely, it is highly possible that these transformative technologies could exacerbate existing health-care inequalities instead.