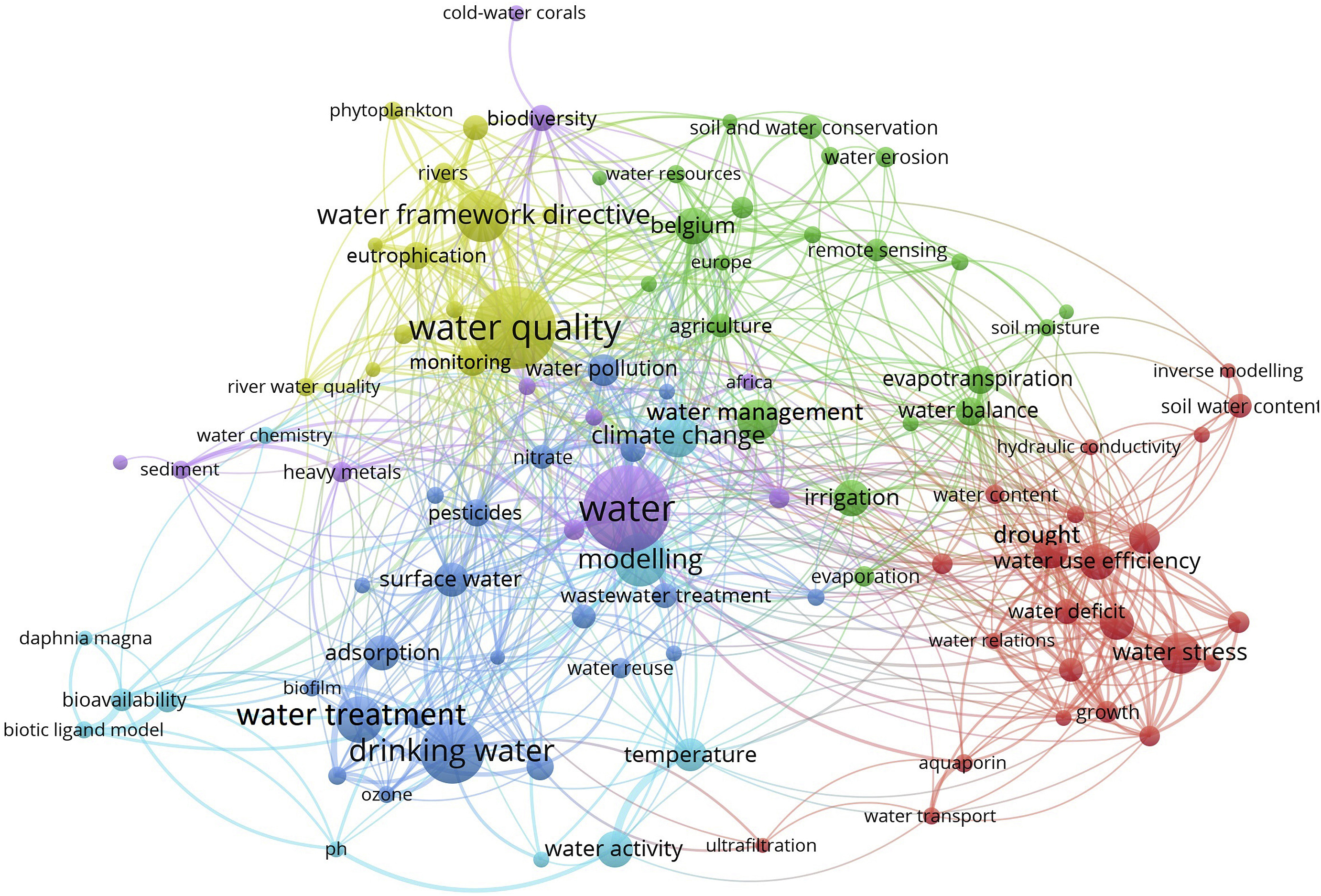
Reaching the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6 on water and sanitation is fundamentally important and conditional to the achievement of all the other SDGs. Nonetheless, achieving this goal by 2030 is challenging, especially in the Global South. Science lies at the root of sustainable development and is a key to new solutions for addressing SDG 6. However, SDG 6-related scientific outputs are often unknown, forming disconnections between academic world and practitioners implementing solutions.
Earth's ecosystems, upon which all life depends, are in a severe state of degradation. The upcoming UN Decade of Ecosystem Restoration aims to “prevent, halt and reverse the degradation of ecosystems on every continent and in every ocean.” These Voices articulate why and what action is urgently needed.
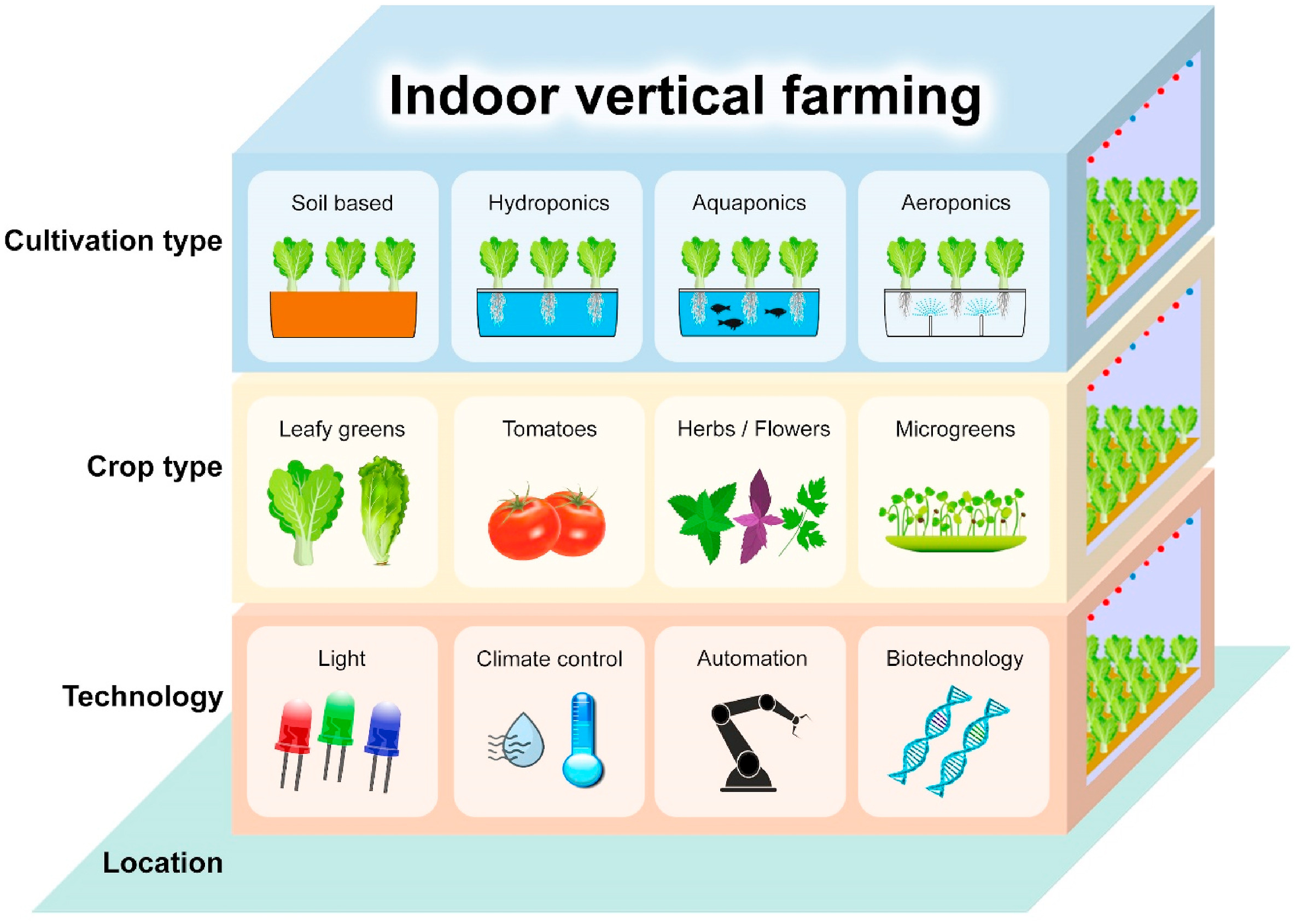
Background: Agricultural production in controlled indoor farming offers a reliable alternative to food and nutrition supply for densely populated cities and contributes to addressing the impending food insecurity. Leafy vegetables, rich in vitamins, minerals, fibres and antioxidants, account for over half of the indoor farming operations worldwide. Light is the foremost environmental factor for plant growth and development, and the success of indoor farming largely depends on lighting qualities.
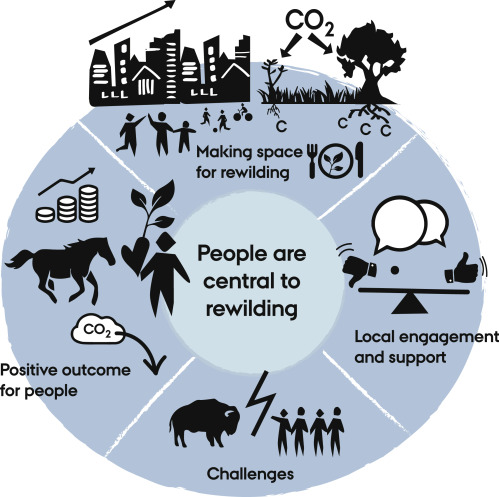
Rewilding should be central to the massive restoration efforts needed to overcome the global biodiversity crisis and enhancing the biosphere's capacity to mitigate climate change. Key elements include large areas for nature, restoration of functional megafaunas and other natural biodiversity-promoting factors, synergy with major societal dynamics, and careful socio-ecological implementation.
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced sudden transformation in many sectors of the global community, turning the world upside down. Everything has been impacted, not excluding the education sector, which has experienced some unforeseen changes in many parts of the world. The sudden transition to online pedagogy as a result of COVID-19 in developing countries has exposed some inequalities and challenges, as well as benefits. These challenges and inequalities have now become the new realities in the educational sector of developing countries.
Agricultural pesticides represent a significant class of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) to which non-target organisms around the world are constantly exposed. Laboratory studies have found strong evidence showing the endocrine-disruptive potential of these pesticides at environmentally relevant exposure levels. Since the field of endocrine disruption continues to grow in richness and complexity, this review aims to provide an update on the effects of two agricultural pesticides that act as EDCs: atrazine and endosulfan.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration has been increasing in the last two decades and, as a major greenhouse gas, it has been linked to global warming and climate changes. Capture and conversion of CO2 into fuels and chemicals offer opportunities to mitigate the increasing CO2 buildup, while simultaneously adding value to CO2. The main limitation in CO2 conversion is its high thermodynamic stability, thus requiring catalysts and energy input to drive the transformation.
Among the major pollutants in the atmosphere, carbon oxides are the result of multiple factors, mainly due to human activities. Nowadays, the decrease in carbon oxides emissions represents a pressing challenge necessary to limit their harmful effects on the climate change. As a result, numerous strategies dedicated to the environmental preservation are currently under study and, among these, all that kind of technologies that produce power from renewable sources offer promising solutions.
In this essay some important forerunners of green chemistry will be discussed and compared with the present state. The relationship to ethics will be considered. Starting from the new movement of green chemistry by Anastas, some important highlights will be presented. The new activities of IUPAC and other institutions on the concepts of metrics for green syntheses will be discussed. The prime importance of the inclusion of developing African countries into the concepts will also be covered.