Biodiversity and ecosystems, encompassing the vast variety of life on Earth and the natural systems they inhabit, are fundamental to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Their importance is acknowledged explicitly in several SDGs due to their critical role in maintaining environmental balance and supporting human life and well-being.
SDG 14 (Life Below Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land) are directly focused on the conservation and sustainable use of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, respectively. These goals recognize the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the vital services ecosystems provide, such as habitat for wildlife, carbon sequestration, and soil formation. The preservation and restoration of ecosystems like forests, wetlands, and coral reefs are essential for maintaining biodiversity, which in turn supports ecological resilience and the sustenance of human life.
The role of biodiversity and ecosystems in achieving SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) is significant. The variety of life forms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, underpins agricultural productivity. Pollinators, soil organisms, and genetic diversity of crops are all crucial for food production and agricultural resilience. Ecosystems support agriculture not just in terms of crop yield but also in sustaining the natural resources like soil and water, upon which agriculture depends.
Similarly, SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) is closely tied to the health of ecosystems. Natural habitats such as forests and wetlands play a key role in filtering and purifying water, maintaining the water cycle, and regulating water flow. This natural filtration process is vital for providing clean drinking water and supporting sanitation systems.
Biodiversity and ecosystems are also crucial for SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being). Natural environments regulate diseases by supporting a balance among species that, in turn, can control pest and disease outbreaks. Additionally, a vast number of medical discoveries, including medicines and treatments, have their origins in biological resources, underscoring the potential of biodiversity in contributing to human health and well-being.
Moreover, biodiversity and ecosystems play a significant role in addressing climate change, linking to SDG 13 (Climate Action). Ecosystems such as forests and oceans are major carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Protecting and restoring these ecosystems are vital strategies for climate change mitigation. Additionally, healthy ecosystems provide crucial services for climate change adaptation, such as protecting against extreme weather events and helping communities adjust to changing environmental conditions.
However, achieving these goals requires addressing threats to biodiversity and ecosystems, such as habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and invasive species. It also involves balancing the needs of human development with environmental conservation, ensuring sustainable use of natural resources.
Biodiversity and ecosystems are integral to achieving multiple SDGs. Their conservation and sustainable use not only benefit the environment but are essential for food security, water purity, human health, and combating climate change. The protection and restoration of biodiversity and ecosystems are therefore crucial steps towards sustainable development and ensuring the well-being of current and future generations.
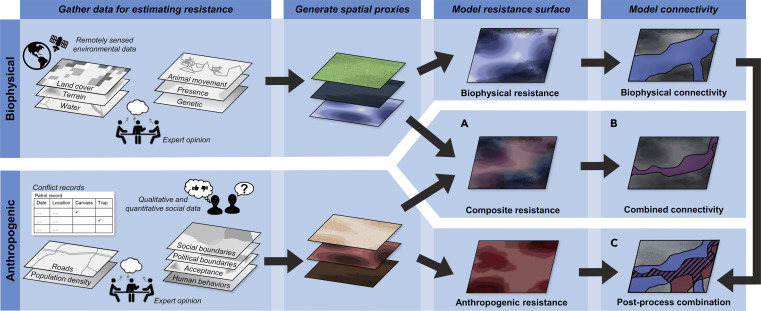
Maintaining or restoring connectivity among wildlife populations is a primary strategy to overcome the negative impacts of habitat fragmentation. Yet, current connectivity planning efforts typically assess landscape resistance, the ability of organisms to cross various biophysical elements in a landscape, while overlooking the various ways in which human behaviors influence connectivity. Here, we introduce the concept of “anthropogenic resistance” to capture the impacts of human behaviors on species' movement through a landscape.
The ability to maintain a (relatively) stable body temperature in a wide range of thermal environments by use of endogenous heat production is a unique feature of endotherms such as birds. Endothermy is acquired and regulated via various endocrine and molecular pathways, and ultimately allows wide aerial, aquatic, and terrestrial distribution in variable environments. However, due to our changing climate, birds are faced with potential new challenges for thermoregulation, such as more frequent extreme weather events, lower predictability of climate, and increasing mean temperature.
Global social and economic changes, alongside climate change, are affecting the operating environment for agriculture, leading to efforts to increase production and yields, typically through the use of agrochemicals like pesticides and fertilizers, expanded irrigation, and changes in seed varieties. Intensification, alongside the expansion of agriculture into new areas, has increased harvest, but has also had numerous well-known impacts on the environment, ultimately resulting in a loss of resilience and lack of sustainability in agro-ecosystems.
Water harvesting techniques have shown promising outcomes in mitigating risks, increasing yields and delivering positive influences on other ecosystems. A field study was conducted in Northern Jordan to assess the influence of combined in-situ water harvesting techniques, micro-catchment and mulching on soil moisture content, plant morphology, gas exchange [photosynthesis (Pn), transpiration (E), and stomatal conductance (gs)] and midday stem water potential (Ψsmd) of young pistachio (Pistacia vera cv. Ashori) trees.