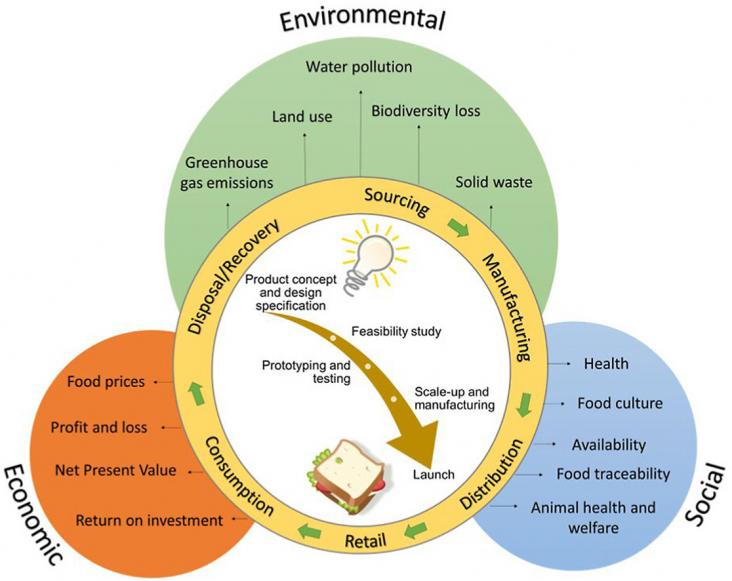
The food industry is responsible for significant impacts on the environment, such as climate change, water depletion and land use.
Background: nationally determined contributions (NDCs) serve to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement of staying “well below 2°C”, which could also yield substantial health co-benefits in the process.
The consumption of meat contributes significantly to undesirable effects on the environment.
Critical knowledge gaps about environmental fate and unintentional effects of currently used pesticides (CUPs) hamper the understanding and mitigation of their global impacts on ecological processes.
This study was conducted to assess the self-reported and observed food safety practices (FSP) of food handlers, who deliver food products that are prepared and cooked at home during the COVID-19 pande
Non-destructive testing techniques have gained importance in monitoring food quality over the years.
Background: Fake meat industry is expected to grow and to be worth $140 billion by 2030. Alternative protein can be produced by plant or microbe.
The consumption of meat contributes significantly to undesirable effects on the environment.

Increasing the production of food from the ocean is seen as a pathway toward more sustainable and healthier human diets.

