Veganism, centered on the avoidance of animal products, particularly in diet, significantly aligns with various Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations. This alignment is multifaceted, influencing goals related to hunger, health, responsible consumption, and environmental sustainability.
Starting with SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), veganism offers a potential solution to global food scarcity. A plant-based diet is typically more resource-efficient, requiring less land, water, and energy compared to animal-based diets. This efficiency could be instrumental in feeding a growing global population, especially in areas where food scarcity is prevalent.
In the context of SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), veganism promotes a more sustainable food production system. It encourages the reduction of waste and efficient use of natural resources. Animal agriculture is known for its high environmental footprint, consuming vast amounts of water and land. By shifting towards plant-based diets, there's a potential for a significant reduction in the ecological impacts associated with food production.
Veganism also has a direct correlation with SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being). A well-planned vegan diet can provide numerous health benefits. It tends to be rich in certain nutrients and lower in saturated fats, which can help in preventing heart disease, obesity, and some types of cancer. It's important to note that a balanced vegan diet, which includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds, is essential to meet nutritional needs.
Moreover, veganism contributes significantly to SDG 13 (Climate Action). Animal agriculture is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. By reducing the demand for animal products, a vegan diet can lower the carbon footprint associated with food consumption.
Regarding SDG 14 (Life Below Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land), veganism can play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity and ecosystems. Animal farming is a leading cause of deforestation, habitat destruction, and species extinction. It also impacts aquatic life through practices that lead to ocean dead zones and overfishing. By decreasing reliance on animal products, veganism can help mitigate these environmental issues.
Veganism's contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals is comprehensive. It addresses critical issues such as hunger, health, responsible consumption, and environmental preservation. By embracing a plant-based diet, individuals can play a part in a more sustainable and equitable world, aligning their personal choices with broader global goals for a better future.
Meat induces large environmental impact while supplying important nutrients, and meat substitutes are increasingly adopted as direct replacers of meat products. This study assessed the environmental impact of a pork schnitzel and two soy-based schnitzels in terms of three different functional units to reflect the products’ functions as meal components and suppliers of high quality proteins. For a functional unit of 1 kg of product, the pork schnitzel induces the largest environmental impact for most environmental impact indicators.
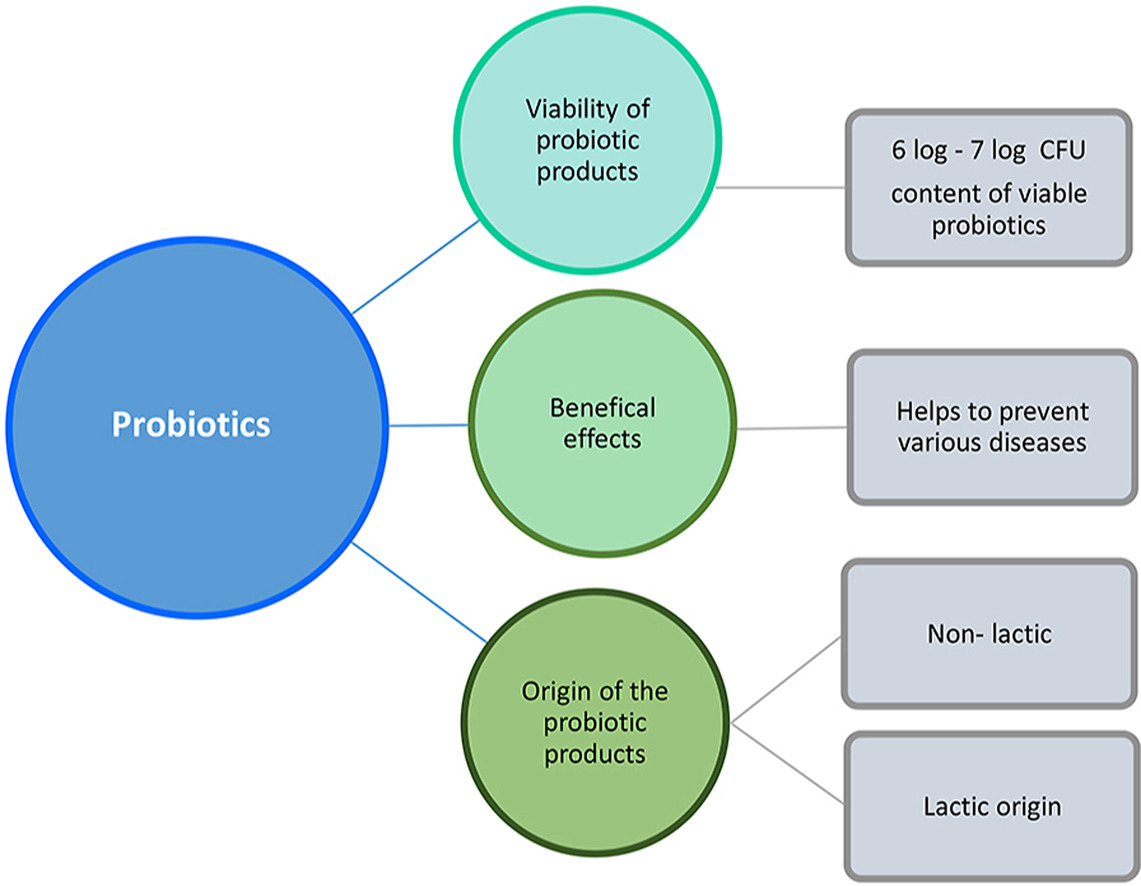
Foods with probiotics are in high demand by consumers given their associated health properties that make them the most popular functional foods. Probiotics have primarily been used in products of lactic acid origin. However, nondairy foods are increasingly being used as carriers of probiotics because the population exhibits high levels of lactose intolerance. In addition, modern lifestyles are increasingly distant from animal food consumption such as dairy products.
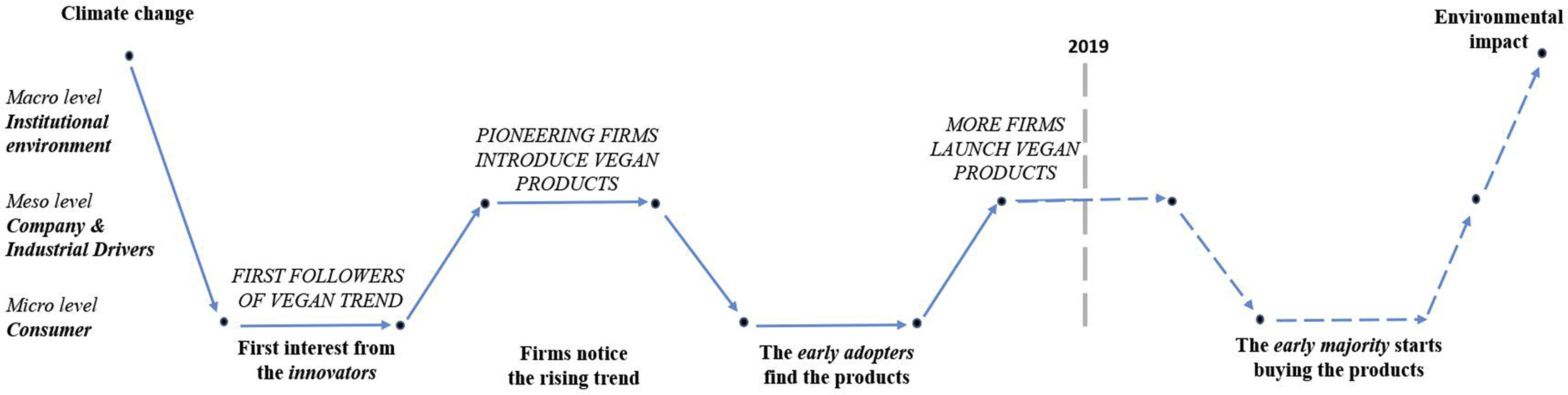
Background: Today's meat and dairy industry has a vast environmental footprint. To reach the UN sustainable development goals (SDGs) of ending hunger globally (SDG #2) and achieving sustainable consumption and production (SDG #12), this food production system needs to change. Recent years have seen the rise in popularity of the vegan or plant-based diet among consumers, which can go some way to reducing the environmental burden.