This article supports SDG 2, SDG 3 and SDG 15 by highlighting the win-win solutions for national parks to both protect nature and improve local people's wellbeing.
This book chapter advances SDG 15 by bringing current bioremediation techniques together to compare, understand, and effectively apply strategies to exclude inorganic pollutants from contaminated environments, keeping in view the effectiveness and economics of bioremediation strategies.
The diversification of tropical pastures with legumes (trees) for increased forage and animal productivity has been advocated.
Viticulture is a valuable sector worldwide with an extraordinary socio-economic impact in Spain.
Fire is an ecological disturbance that alters soil microbiomes and the functions they mediate in terrestrial ecosystems.
The biochemical effects of trees may significantly influence local pedogenesis as well as pedocomplexity, biodiversity and forest dynamics on both stand and landscape scales.

Each year, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) celebrates World Food Day on October 16th to commemorate is founding in 1945. World Food Day 2020 is calling for global solidarity to help all populations to recover from the crisis, and to make food systems more resilient and robust so they can withstand increasing volatility and climate shocks, deliver affordable and sustainable healthy diets for all, and decent livelihoods for food system workers. In support of this years theme - 'Grow, Nourish, Sustain. Together' - Elsevier presents a curated, open access collection of 40 journal articles and book chapters focussed on increasing food security and sustainability.
Elsevier,
Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part - C: Toxicology and Pharmacology, Volume 235, September 2020
This article advances SDG # 15 and # 14 by looking at the potential adverse effects relatively high total mercury concentration has on the developing fetus of Steller sea lions.
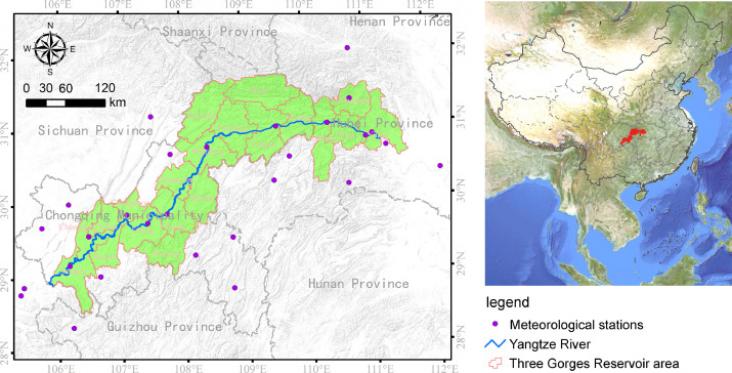
Climate, land use and land cover (LULC) changes are among the primary driving forces of soil loss.
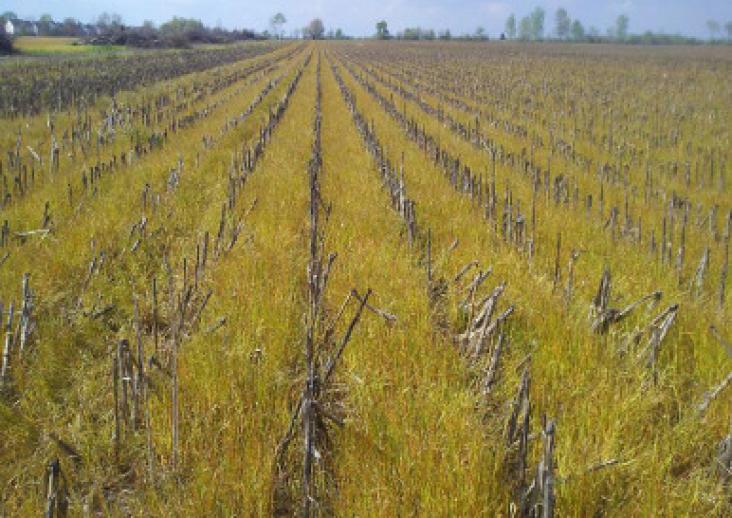

Tillage is the most common agricultural practice dating back to the origin of agriculture. In recent decades, no-tillage (NT) has been introduced to improve soil and water quality.
