Elsevier,
Global Food Security,
Volume 27,
2020,
100442,
ISSN 2211-9124,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100442.
This paper provides an overview of children and adolescents’ diet. Food systems need to be redesigned to improve diet quality in children 0-19 years in order to address the multiple burdens of malnutrition. Data systems also need to be strengthened to track data quality among children. This article advances knowledge on SDG 2 and 3.
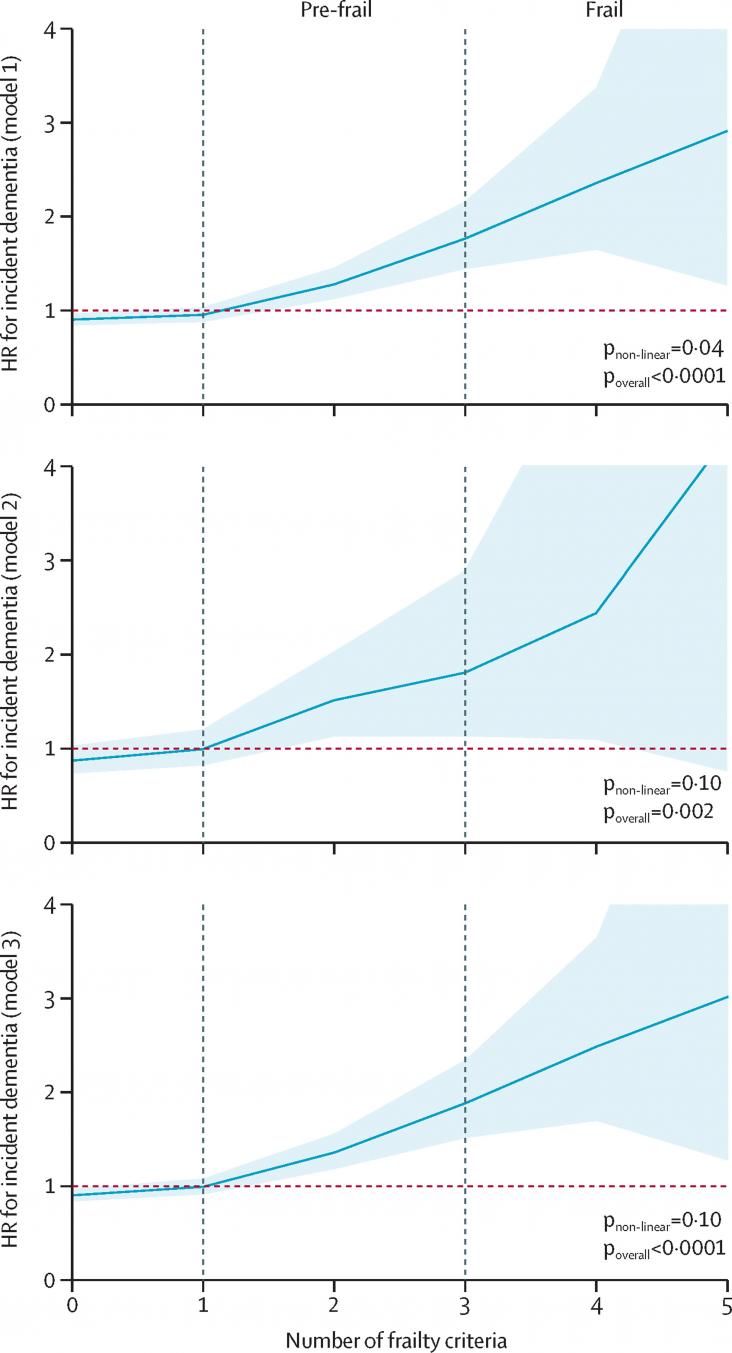
An article on dementia incidence, in the context of SDG 3, focusing specifically on the association between physical frailty and all-cause dementia in the UK.
This article supports SDG 2, SDG 3 and SDG 15 by highlighting the win-win solutions for national parks to both protect nature and improve local people's wellbeing.
Partner content
Global CitizenGlobal Citizen, 26th October 2020
COVID-19 testing in Africa has so far been limited to larger cities because of how the tests are conducted, which means that it is far more difficult to test those in remote and rural areas where there are higher rates of poverty. The United Nations’ Global Goal 3 promotes good health and well-being for all, and this can only be achieved if all people in all places have access to health care and virus testing.

Social media assemble multiple users' interactions across singular events. Authorities need to navigate this diversity to effectively communicate and promote collaborative strategies.
This journal article advances SDG 3 and 10 by explaining that racial discrimination has no place in society, and certainly, not in this time of COVID-19 pandemic. As the epicentre of the disease outbreak continues to shift from place to place, urgent measures need to be developed to reduce the increasing cases of racial discrimination.
Objective: To examine the psychological distress and the associated predictor factors of the 2019 corona-virus disease (COVID-19) on survivors in the early convalescence in Shenzhen.
Background: There are growing numbers of adults aging with long-term mobility disabilities.

Due to advances in the early detection of Alzheimer's disease (AD) biomarkers including beta-amyloid (Aβ), neuropsychological measures that are sensitive to concurrent, subtle changes in cognition are
