This Article supports SDG 3 and 5 by highlighting a need for greater involvement of in-country authors on research examining a wider range of gendered COVID-19 impacts, as well as increased representation of diverse topics and publications related to COVID-19 and women's well-being focused on lower income countries.
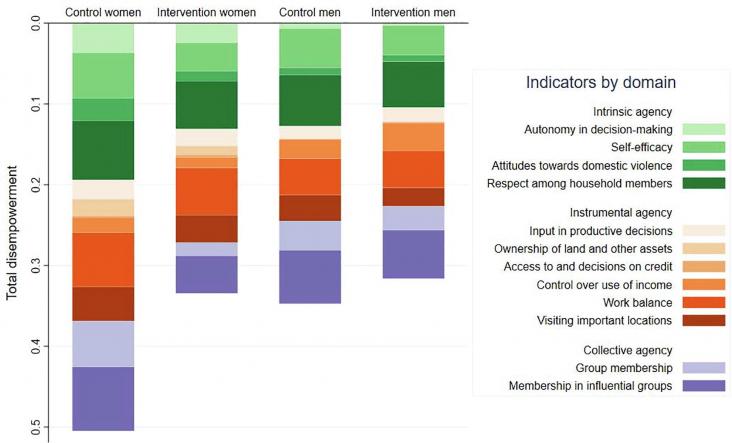
This Study supports SDG 5 and 3 by examining the role of improved women's agency on the pathway from the intervention to nutritional impacts.
This Article supports SDGs 5, 8, and 10 by investigating the prevalence of workplace sexual harassment and violence by demographic factors and work sectors among Icelandic women, providing nuanced targets for prevention and for public policies aimed at promoting women’s safety in the work environment.
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 5, describing intimate partner violence within military communities and drawing comparisons with a general population cohort.
An investigation, linking particularly well to SDGs 10 and 5 focusing on equality, which shows how researchers can actively engage with equality, diversity and inclusion (EDI) in their work, and how EDI considerations must remain an ongoing effort. The authors, working in the field of responsible research and innovation (RRI), intentionally employed EDI in their project recruitment, and reflect here on the adjustments they made as a result. The recruitment of persons with disabilities led to some particularly interesting and new insights in this study looking at trustworthiness in the design of autonomous systems with evolving functionality.
This Review supports SDGs 3 and 5, focusing on the gendered association between unpaid labour and mental health, particularly in relation to the fact that women do more hours of unpaid labour worldwide than men. The Review found that unpaid labour is associated with worse mental health in women than in men.
This Article supports SDG 5 by examining factors associated with implementation of organisational interventions for advancing women in health-care leadership.
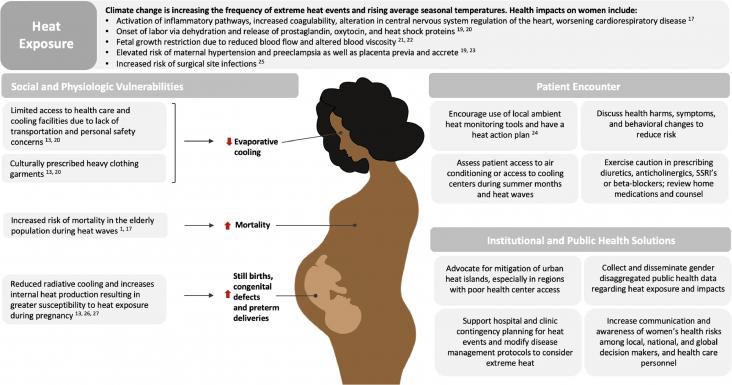
Climate change threatens to widen existing gender-related health disparities as well as socioeconomic disparities among women.
Experience of domestic violence has been suggested as a risk factor for diabetes. Longitudinal data from 5782 Australian women over 20 years were analysed. Childhood sexual abuse and intimate partner violence predicted subsequent diabetes. The association was only partly attenuated when obesity was taken into account. Awareness of a history of abuse may help in the management of obesity and diabetes in women.
Examines multiple forms of adolescent violence perpetration across gender, racial/ethnic, and sexual identities. Boys reported greater rates of perpetration than girls, except for teen dating violence. Perpetration rates did not differ for intersection of gender by race/ethnicity. Perpetration rates varied across racial/ethnic, sexual, and gender minority students compared to non-minority students.
