Purpose and setting: Infrastructure is a global multi-trillion dollar market presenting many opportunities and risks for sustainable development.
The process industries have been facing ever increasing pressure in the monitoring and control of gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds and hazardous air pollutants.
The successful conversion of lignocellulose into value-added products depends on overcoming the recalcitrance of its structure towards enzymatic digestion.
Bio-based aerogels with customizable porosities and functionalities constitute a significant potential for CO2 capture.
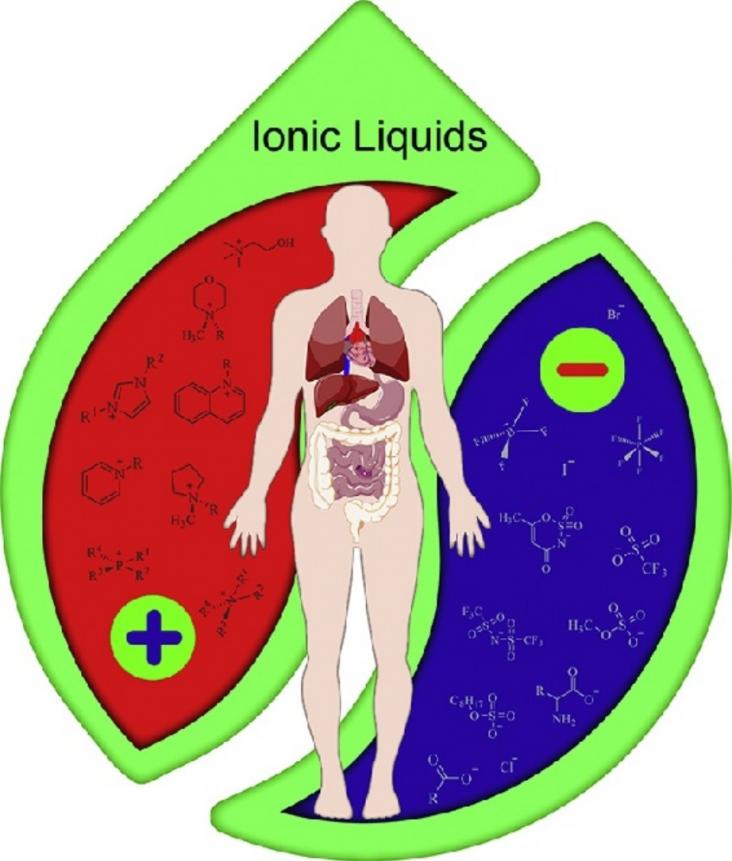
Beyond their traditional use as green solvents, new applications have become available for ionic liquids (ILs) in drug delivery.
In this paper, an integrated blockchain-based energy management platform is proposed that optimizes energy flows in a microgrid whilst implementing a bilateral trading mechanism.
There is a wide array of biomass utilisation pathways to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
The potential of electron-donating capability in methoxy groups of antioxidant containing protein (ACAP) as organic catalyst is restricted by its low isoelectric point.
Although deployments of grid-scale stationary lithium ion battery energy storage systems are accelerating, the environmental impacts of this new infrastructure class are not well studied.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have an established role in the consumer electronics markets with minimum risk of replacement from any other contender in the near future.
