April 7th of each year marks the celebration of World Health Day. From its inception at the First Health Assembly in 1948 and since taking effect in 1950, the celebration has aimed to create awareness of a specific health theme to highlight a priority area of concern for the World Health Organization.
Over the past 50 years this has brought to light important health issues such as mental health, maternal and child care, and climate change. The celebration is marked by activities which extend beyond the day itself and serves as an opportunity to focus worldwide attention on these important aspects of global health.
In recent years, countries in the Western Pacific have experienced rapid economic growth, migration and urbanization. This created opportunities for better lives for many, but left others behind. The COVID-19 pandemic has undercut recent health gains, pushed more people into poverty and food insecurity, and amplified gender, social and health inequities.
This World Health Day, we’re calling for action to eliminate health inequities, as part of a year-long global campaign to bring people together to build a fairer, healthier world. The campaign highlights WHO’s constitutional principle that “the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of health is one of the fundamental rights of every human being without distinction of race, religion, political belief, economic or social condition.”
To mark World Health Day 2021, Elsevier presents a curated list of free access journal articles and book chapters in support of this year's theme - building a fairer, healthier world for everyone.
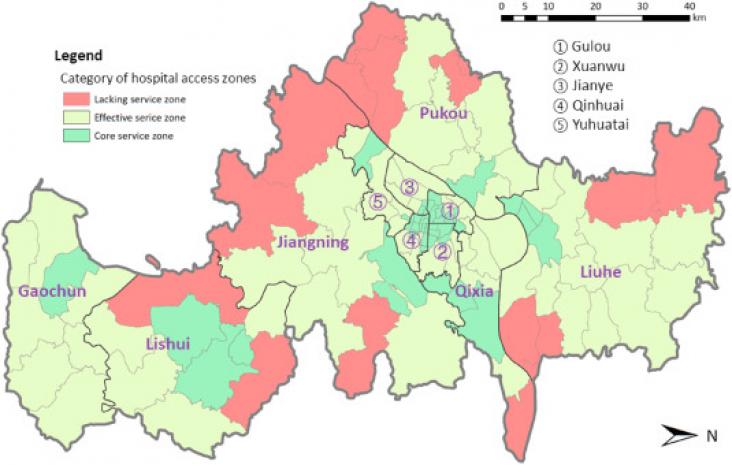
Journal of Transport and Health, Volume 19, December 2020
Background: With the rapid demographic shift towards an ageing society, it is a concerted effort to facilitate elderly's access to healthcare in order to maintain and improve their quality of life. In China, hospital care services dominate the healthcare market, which requires a better understanding of accessibility to hospitals in order to rationally allocate resources in spatial and land use planning. However, little attention has been paid to analysing the geographical accessibility to hospitals specific to the elderly population.
Intelligence-Based Medicine, Volume 3-4, December 2020
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is one of the leading causes of preventable blindness in the working-age diabetic population in India and across the world. It may lead to permanent blindness if not detected in the early stages. The prevalence of DR among diabetics in India was 10% and 16.9% in 2014 and 2019, respectively. In 2019, the International Diabetes Federation estimated that Diabetic Mellitus will affect 101 million people in India in 2030; the largest number in any nation in the world.
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update, Volume 1, 2021, 100005
Psychology and Climate Change, 2018, Pages 95-124
Social Ecology in the Digital Age, 2018, Pages 265-317
The Developing Microbiome, 2020, Pages 21-41
Clinical and Translational Perspectives on Wilson Disease, 2019, Pages 354-353
Effects of Lifestyle on Men's Health, 2019, Pages 149-168
Chronic Kidney Disease in Disadvantaged Populations, 2017, Pages 273-289
Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, Volume 94, 2020, Pages 1-34
Food, Medical, and Environmental Applications of Polysaccharides, 2021, Pages 381-400
Gemma C. Cotton, Natalie R. Lagesse, Liam S. Parke, Carla J. Meledandri, 3.04 - Antibacterial Nanoparticles, Editor(s): David L. Andrews, Robert H. Lipson, Thomas Nann, Comprehensive Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (Second Edition), Academic Press, 2019, Pages 65-82
Immunology and Allergy Clinics of North America, Volume 41, February 2021
Increased levels of CO2 and various greenhouse gases cause global warming and, in combination with pollutants from fossil fuel combustion and vehicular and industrial emissions, have been driving increases in noncommunicable diseases across the globe, resulting a higher mortality and morbidity. Respiratory diseases and associated allergenic manifestations have increased worldwide, with rates higher in developing countries. Pollen allergy serves as a model for studying the relationship between air pollution and respiratory disorders.
Gastroparesis, 2021, Pages 494-505
Clinics in Chest Medicine, Volume 42, March 2021
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) occurs in women more than men whereas survival in men is worse than in women. In recent years, much research has been carried out to understand these sex differences in PAH. This article discusses clinical and preclinical studies that have investigated the influences of sex, serotonin, obesity, estrogen, estrogen synthesis, and estrogen metabolism on bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II signaling, the pulmonary circulation and right ventricle in both heritable and idiopathic pulmonary hypertension.
Translational Biotechnology, 2021, Pages 53-77
Nanoengineering in Musculoskeletal Regeneration, 2021, Pages 105-136
Principles of Tissue Engineering, Fifth Edition, 2020, Pages 1585-1591
Stem Cells, Third Edition, 2021, Pages 383-399
Organ Repair and Regeneration, 2021, Pages 273-284
Diabetes Digital Health, 2020, Pages 145-157
Obesity, 2020, Pages 117-139
Sex Differences in Cardiac Diseases, 2021, Pages 539-565