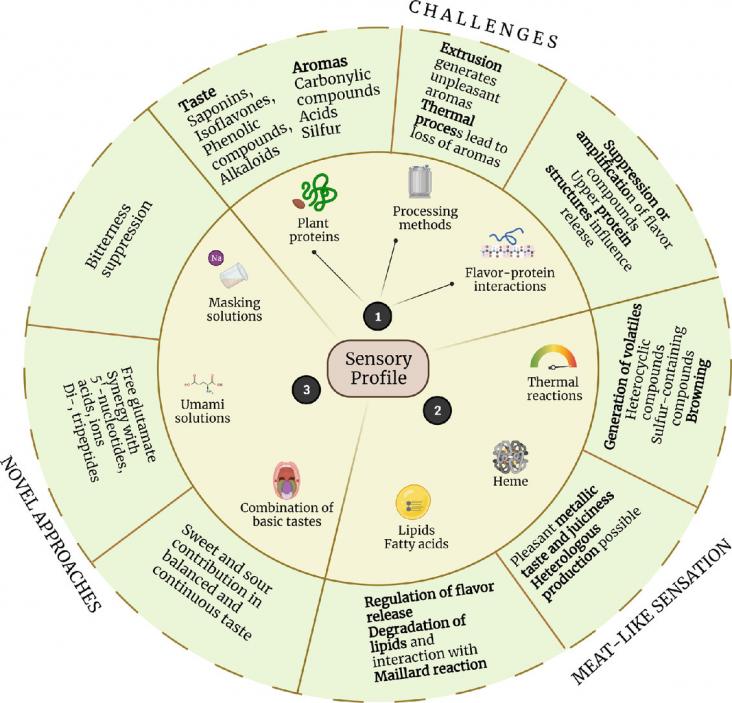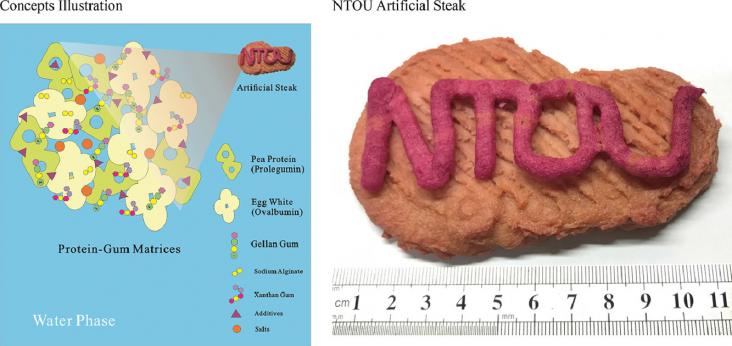
Several studies have indicated that a global reduction in meat consumption is inevitable for sustainability and public health, despite the challenges inherent to changing eating habits.
The availability of food is the basic entity for the survival of human. The resources that make a nation food secured is guided by multiple factors and can be evaluated using a set of indicators.
Transitioning toward plant-based diets can alleviate health and sustainability challenges.
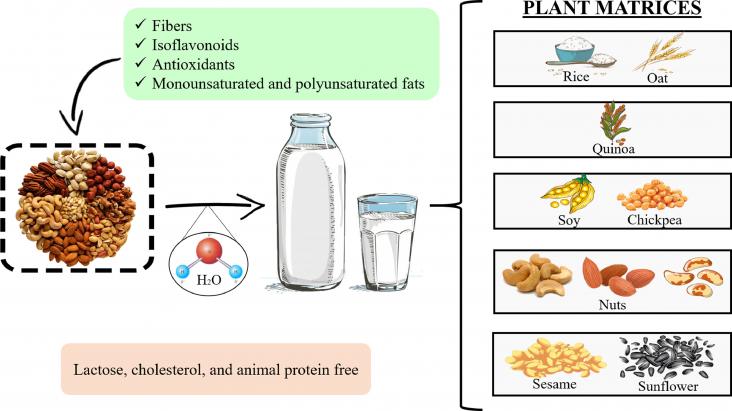
Cow's milk is considered a staple in many diets due to its high nutritional value. It contains almost every nutrient that the human body needs.
Meat induces large environmental impact while supplying important nutrients, and meat substitutes are increasingly adopted as direct replacers of meat products.
Contamination of urban-garden vegetables with potentially toxic elements is a great problem in developing countries. This study assessed the level of PTEs (Cu, Pb, Cr and Cd) in market-sold vegetables in southwest Nigeria and evaluated the estimated daily intake (EDI) to understand the health implications.
A Health Policy paper on the health impacts of banned pesticides in the Yaqui population in Mexico, in the context of SDGs 3, 10, and 12, highlighting recommendations for system-level solutions and policy change to current US, UN, and global laws.
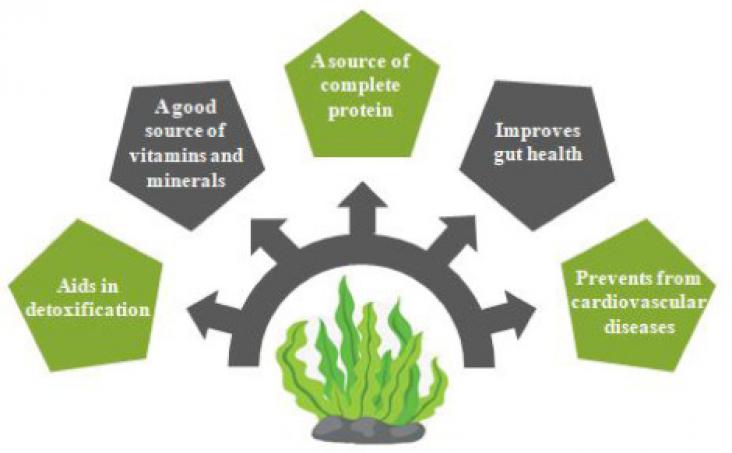
The eminent protein sources among the vegetarian population include cereals and pulses that do not satisfy the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) level.