A study by Snoussi et al., 2024 proposes a methodology for evaluating excavated material's environmental, geotechnical, and agronomical properties to determine its ecological reuse potential, particularly for constructing soil in urban green infrastructure. Through the SWOFI framework (Safety, Workability, Fertility, Infiltrability), the authors characterised a non-cohesive sedimentary parent rock with a sandy loam texture from Bou Argoub in Tunisia. The method successfully assessed the material’s pollution hazard, compaction sensitivity, and fertility showcasing a novel integrated approach for sustainable soil construction in urban landscapes.
Soil systems play a key role in the fight against climate change. A paper, produced by Rubio et al., 2024, highlights the importance of soil management and land conservation for sustainable use of resources. It calls for a comprehensive vision recognizing soil's socio-economic benefits and ecological functions, urging for radical environmental, social, and economic shifts to address climate change responsibly for present and future generations, in alignment with initiatives like the European Green Deal and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Areas prone to drought and land degradation need effective water management plans to secure food production. Methods such as hydrological modelling and digital soil mapping can aid in evaluating water availability (water content and water stress). A study by Horta et al., 2023 examined the use of a global and local soil hydraulic properties (SHP) dataset to simulate soil-water balance at a regional scale in Portugal and found that the SHP dataset is a key factor to consider. The results showed that the choice between global and local SHP datasets significantly impacts the accuracy of soil-water balance simulations, influencing irrigation schedules and potentially jeopardizing crop production and soil quality, particularly in Mediterranean conditions.
This study emphasizes the importance of adopting nexus approaches in Arctic governance to address the complex interactions between climate change, biodiversity loss, land use pressures, and local livelihoods. While Arctic policies often incorporate nexus elements, there is a need to better recognize the agency and impact of local communities and traditional livelihoods in decision-making processes. This aligns with the goals of the International Day of Indigenous Peoples by highlighting the significance of involving indigenous communities in environmental governance and promoting cross-sectoral policies that consider their perspectives and contributions.
The paper addresses the urgency of communicating the worsening anthropogenic-driven species extinction crisis to diverse audiences and proposes a threatened species recovery report card as a tool to showcase conservation progress, emphasizing the need for immediate action to prevent further biodiversity loss.
How to reduce human-wildlife conflixt through education
This study underscores the importance of recognizing and respecting diverse worldviews, knowledge systems, and values in addressing global challenges like biodiversity loss and climate change. By providing a framework that emphasizes understanding onto-epistemological assumptions and power dynamics, the research offers principles to guide more inclusive and respectful engagement with diverse perspectives, aligning with the goals of the International Day of Indigenous Peoples to promote cultural diversity and indigenous knowledge in conservation efforts.
The cascading effects of biodiversity decline on human well-being present a pressing challenge for sustainable development.
Shows behavioural and physiological responses to habitat change
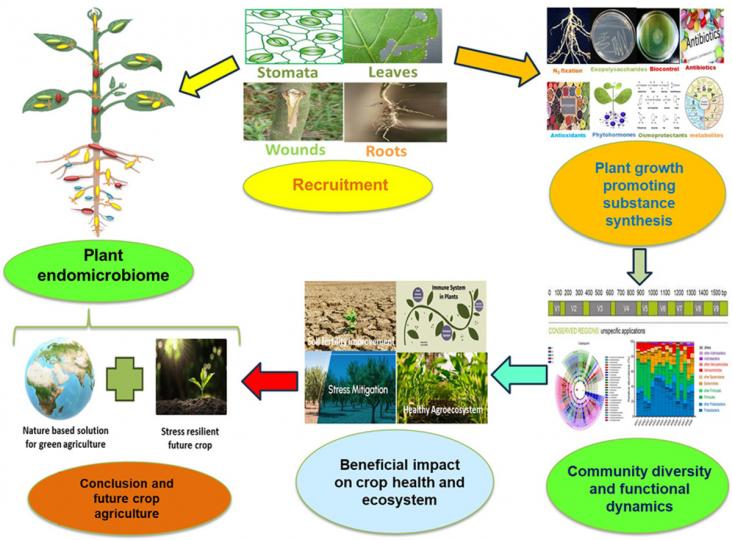
Plants have a microbiome, a diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, living inside and on their tissues. This review article contains deeper insight in endomicrobiome related research work in last years, recruitment, niche development, nutrient dynamics, stress removal mechanisms, bioactive services in plant health development, community architecture and communication, and immunity interplay in producing stress resilient future crop.
