This article advances SDG # 3, 13, and 15 by demonstrating a clear increase in heat-related illness incidence that parallels the temperature elevations from climate change.
This Review supports SDGs 3, 10, and 15 by examining evidence on Indigenous People's mental health related to resource industries in settler colonial states. It shows that land is central to Indigenous people's mental health, and that land dispossession due to industrial development negatively impacted mental health in Indigenous communities.
Castellanos-Barliza and León-Peláez 2023 investigated the recovery of physical-chemical and biological properties of Technosols in a chronosequence of drylands (over 7,10 and 21 years) in the El Cerrejón coal mine in Colombia. Their results showed significant improvements in soil properties, especially near the surface, with notable increases in soil N content and P solution after 7 years. Enhanced vegetation development over time contributed to higher soil organic matter, indicating successful rehabilitation and positive impacts of the restoration strategy in degraded mine spoils.
This article advances SDG # 13, 14, and 15 by arguing that ecosystem integrity is neglected but important for climate adaptation goals, and shows how linking ecosystem integrity to climate, biodiversity and sustainable development goals is crucial for optimal outcomes.
This opinion highlights how tapping into natural biodiversity, while incorporating information about local environmental and climatic conditions, enables crop production in marginal soils.
This study provides a better understanding of the burrowing behaviour of the sub-legal size clams discarded on the sediment after being disturbed and contributes important data to improve practices for minimizing mortality of dislodged clams that are discarded on the sediment surface.
Results from this study contribute to define a complete set of environmental and social data and information, which can help European decision makers to define new criteria for sustainable management of the waste plastics of interest. A new methodological approach has been proposed: it appears able to be applied in future research projects involving innovative management options.
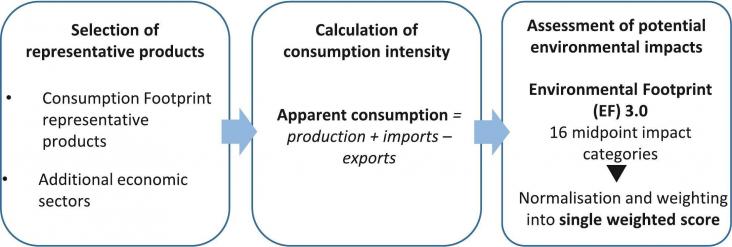
This paper explores the potential implementation of the Consumption Footprint rationale to define a footprint indicator for the EU Bioeconomy, henceforth ‘Bioeconomy Footprint’. This indicator can be a powerful tool for a comprehensive and effective monitoring of the bioeconomy sectors: to capture environmental impacts over time, identifying environmental hotspots, highlighting geographic and sectorial trade-offs, and identifying burden shifts among impact categories and along the supply chain.
This study aims to identify the factors that constrain and enable the sustainability of reusable packaging systems, considering environmental, economic, social and technical dimensions. This research is critical to the effective implementation and scale-up of reusable packaging systems.
This article links with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by addressing Goal 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and Goal 15 (Life on Land), as it examines how urbanization affects biodiversity and the traits that enable bird species to adapt to urban environments. By developing a predictive framework for urban tolerance, the research contributes to conservation efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity in increasingly urbanized landscapes, thereby promoting sustainable coexistence between human populations and wildlife.
