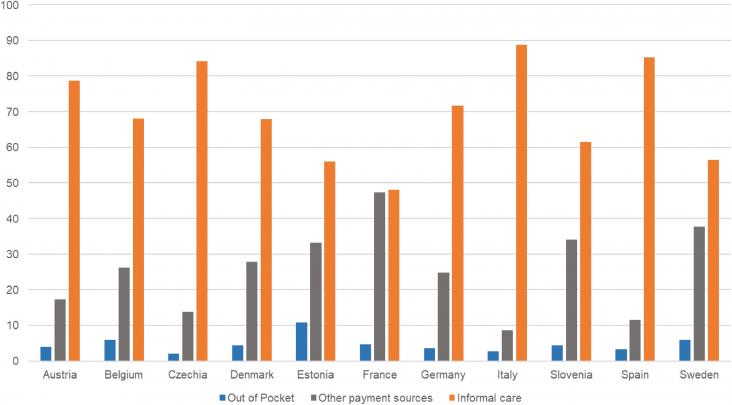
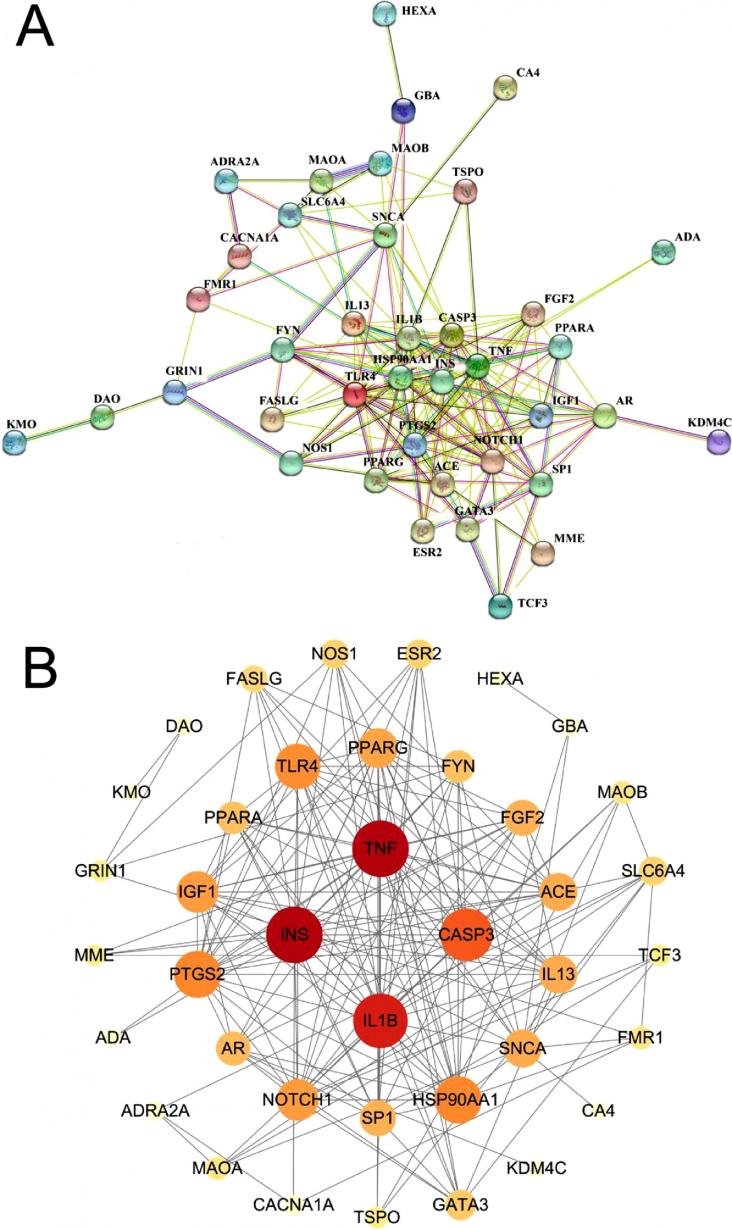
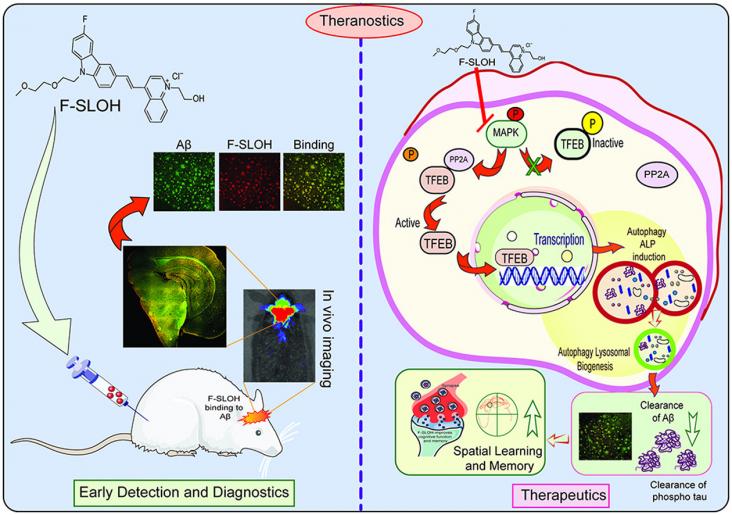
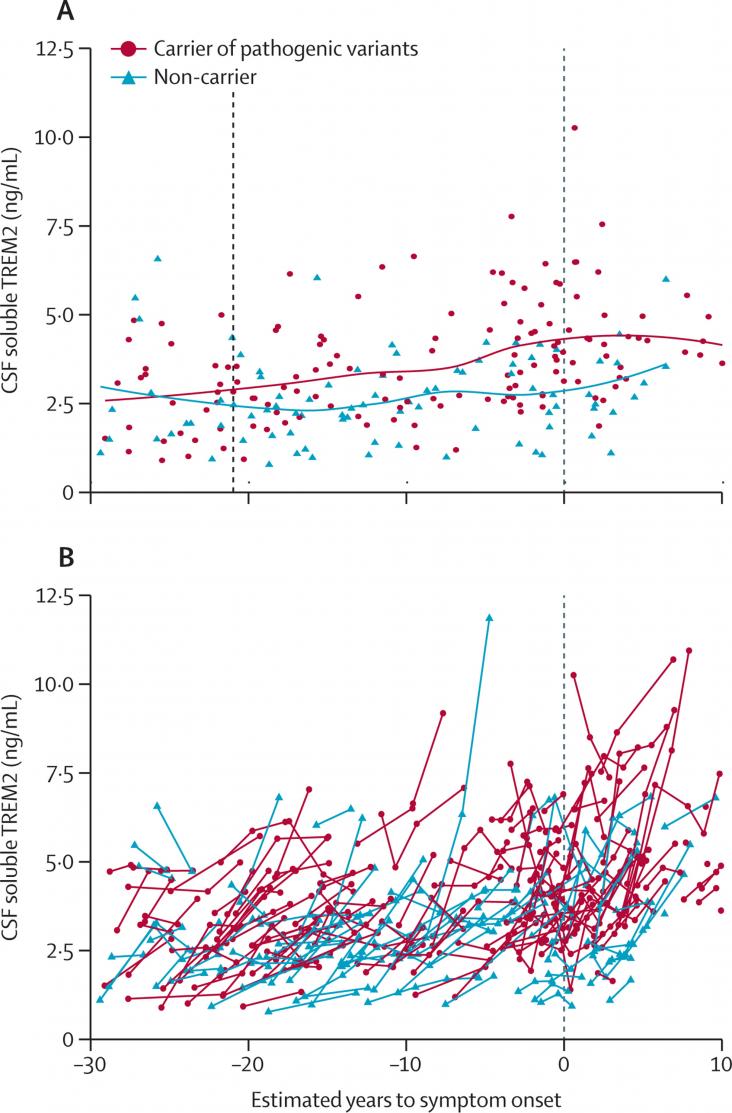
An estimated 50 million people around the world currently live with Alzheimer's disease or other dementias, dementia being a collective term for progressive syndromes that affect various expressions of cognitive function, such as memory and emotional expression. Alzheimer’s disease accounts for the majority of cases (50 to 70%, varying by country, based on Alzheimer’s Disease International and World Health Organization figures). For those directly affected and their loved ones, dementia can be a frightening experience, particularly as it is so poorly understood. However there remains little or no understanding of dementia in many, and the stigmatization and misinformation that surrounds dementia remains a global issue.
For 2022 World Alzheimer’s Day the theme Know Dementia, Know Alzheimer’s, organized annually by Alzheimer’s Disease International, focuses on diagnosis, the warning signs of dementia, with a special focus on post-diagnosis support. The aim of this international campaign is to highlight the importance of support for people living with dementia and families following a diagnosis.
Current Topics in Developmental Biology, Volume 148, January 2022
The Neurobiology of Aging and Alzheimer Disease in Down Syndrome, Volume , 1 January 2021
The Neurobiology of Aging and Alzheimer Disease in Down Syndrome, Volume , 1 January 2021
The Neurobiology of Aging and Alzheimer Disease in Down Syndrome, Volume , 1 January 2021
Alzheimer’s Disease: Understanding Biomarkers, Big Data, and Therapy, Volume , 1 January 2021
Handbook of Decision Support Systems for Neurological Disorders, Volume , 1 January 2021
Alzheimer’s Disease: Understanding Biomarkers, Big Data, and Therapy, Volume , 1 January 2021
Sex and Gender Differences in Alzheimer’s Disease, Volume , 1 January 2021
Alzheimer’s Disease: Understanding Biomarkers, Big Data, and Therapy, Volume , 1 January 2021
Autophagy in Health and Disease, Volume , 1 January 2021
Diagnosis and Management in Dementia: The Neuroscience of Dementia, Volume 1, Volume , 1 January 2020
Handbook of Mental Health and Aging, Volume , 1 January 2020
Neuroprotection in Alzheimer's Disease, Volume , 20 January 2017
Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Volume 179, January 2021
Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Volume 184, January 2022
Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease, 2016, Pages 3-23
Diagnosis and Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury, 2022, Pages 27-38
Diseases of the Nervous System (Second Edition), 2021, Pages 81-107
Exercise to Prevent and Manage Chronic Disease Across the Lifespan, 2022, Pages 413-421
Genetics, Neurology, Behavior, and Diet in Dementia, The Neuroscience of Dementia, Volume 2, 2020, Pages 833-847
Human Caspases and Neuronal Apoptosis in Neurodegenerative Diseases, 2022, Pages 69-151
Nanomedical Drug Delivery for Neurodegenerative Diseases, 2022, Pages 223-242
Neurobiology of Brain Disorders (Second Edition), Biological Basis of Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders, 2022, Pages 313-336
Neurochemical Aspects of Alzheimer's Disease Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, Biomarkers, and Potential Treatment Strategies, 2017, Pages 47-91
Plant Extracts in Neurodegenerative Diseases, 2022, Pages 1-15
Redox Biology, Volume 51, May 2022
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Volume 226, March 2022
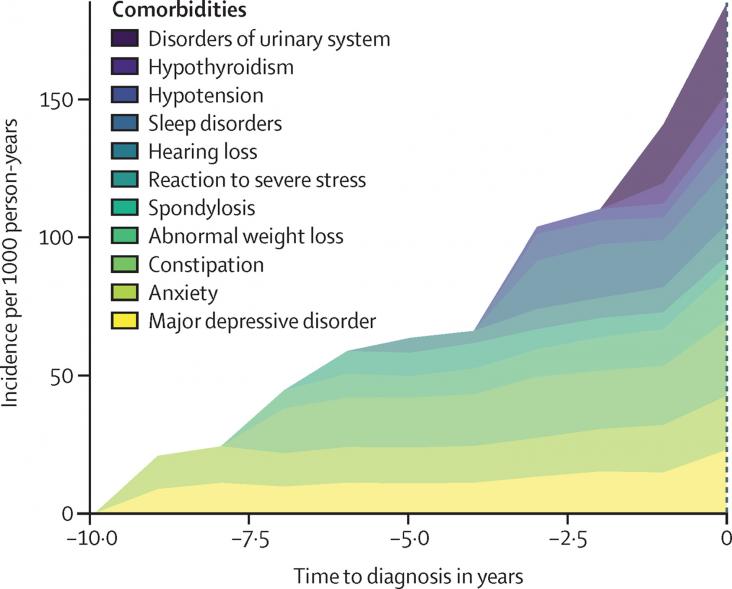
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 7, February 2022
EClinicalMedicine, Volume 39, September 2021
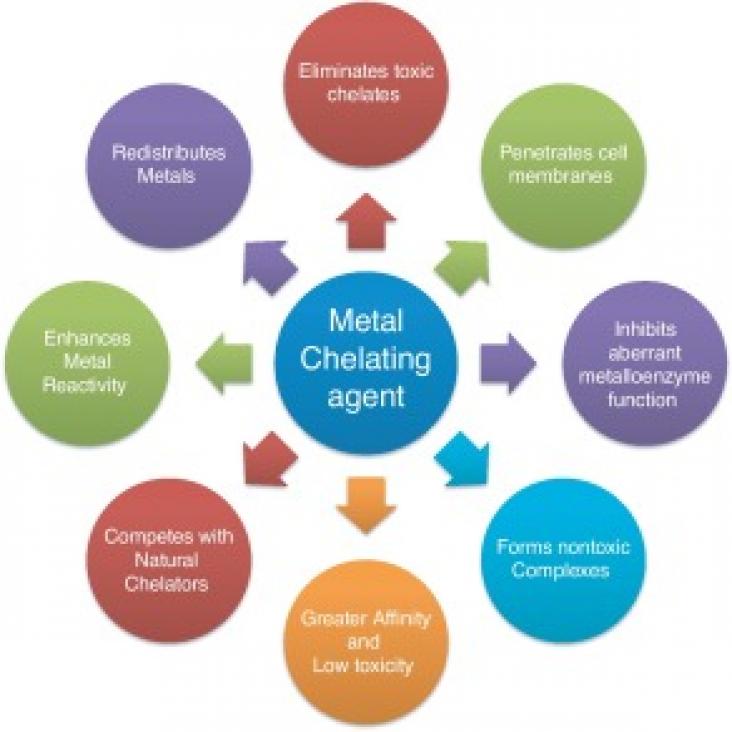
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, Volume 67, September 2021
The Lancet, Volume 396, 8 - 14 August 2020
Redox Biology, Volume 34, July 2020
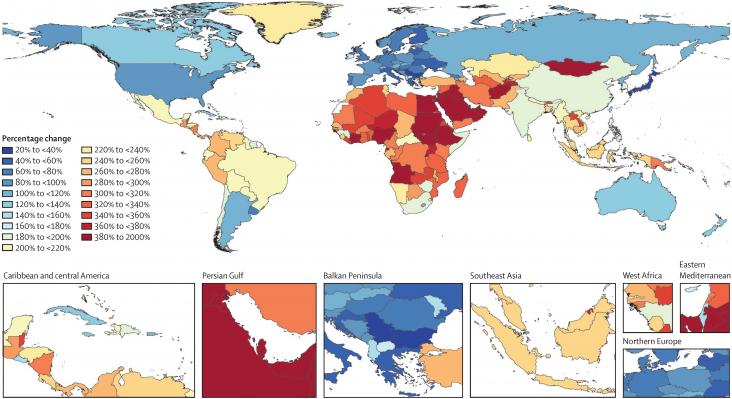
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 8, April 2020
Free Radical Biology and Medicine, Volume 162, January 2021
Mitochondrion, Volume 64, May 2022
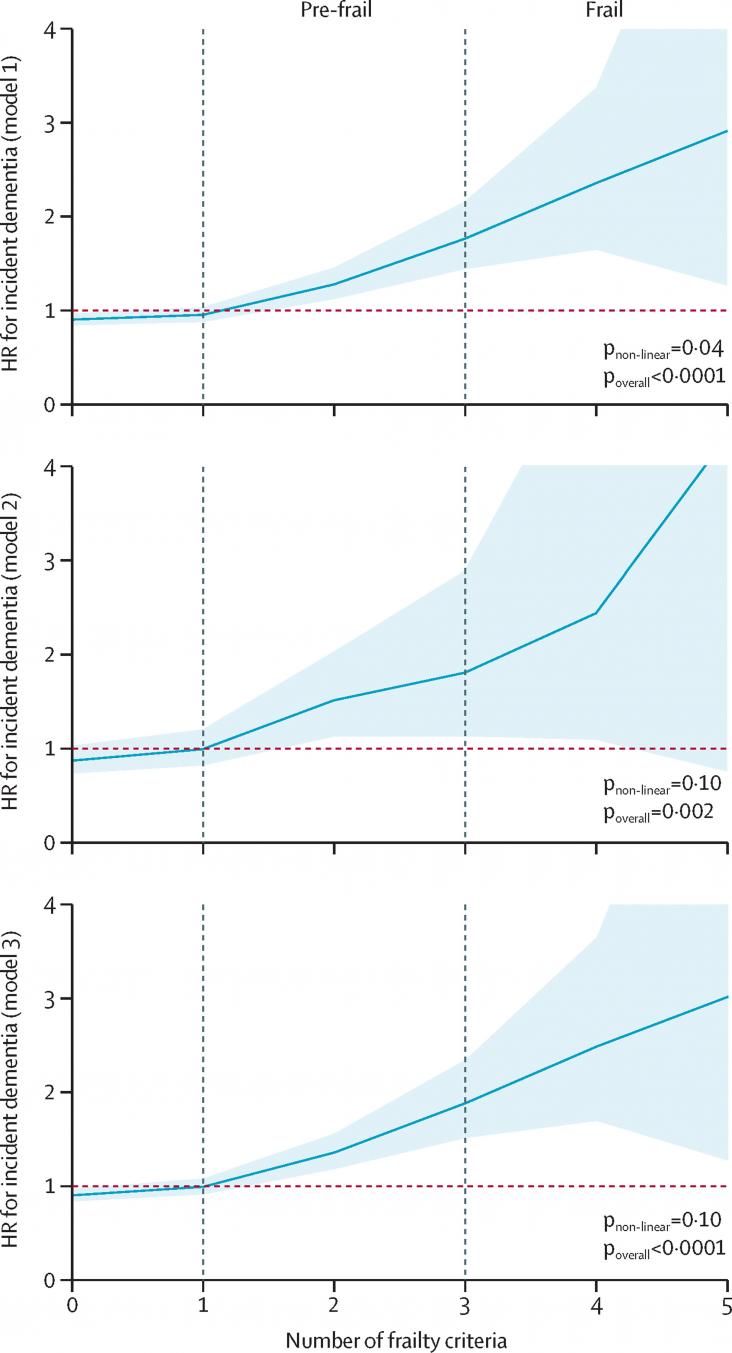
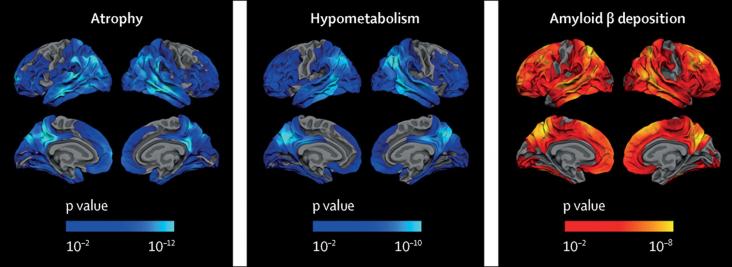
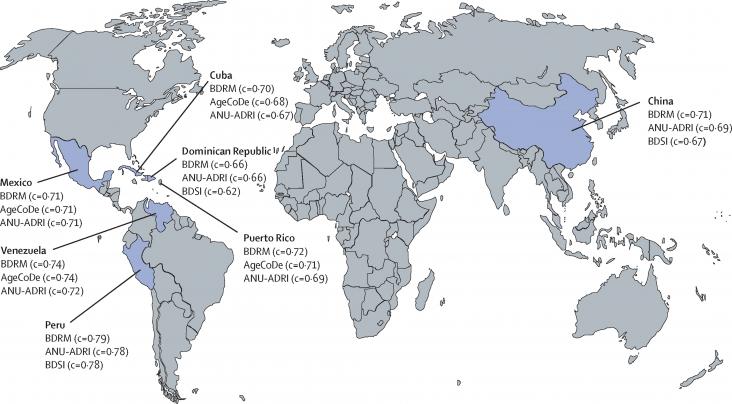
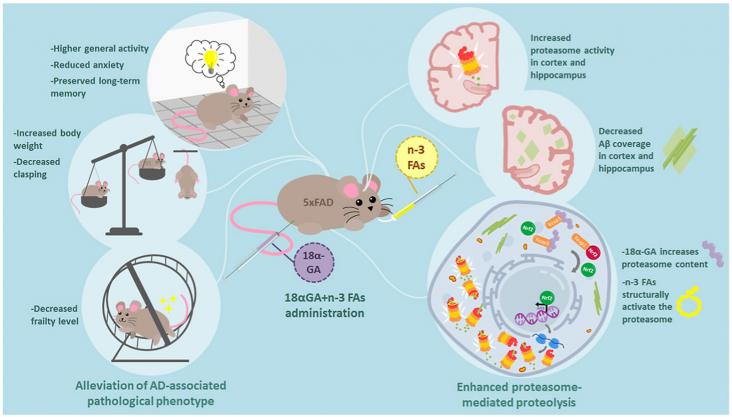
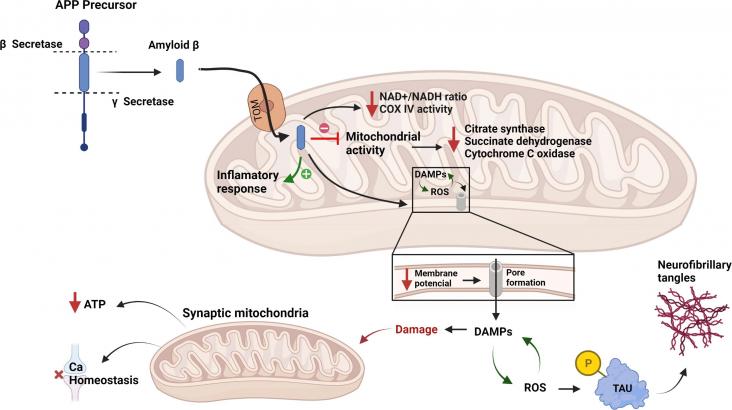
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a leading neurodegenerative pathology associated with aging worldwide. It is estimated that AD prevalence will increase from 5.8 million people today to 13.8 million by 2050 in the United States alone. AD effects in the brain are well known; however, there is still a lack of knowledge about the cellular mechanisms behind the origin of AD. It is known that AD induces cellular stress affecting the energy metabolism in brain cells.
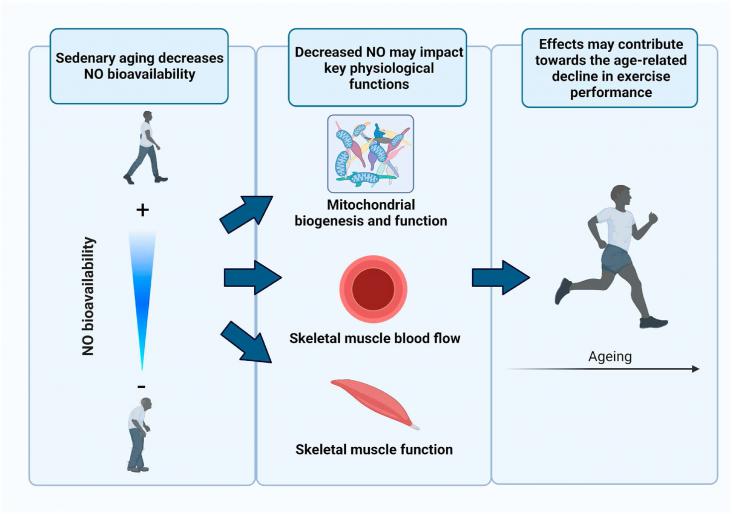
Nitric Oxide - Biology and Chemistry, Volume 125-126, 1 August 2022
SLAS Discovery, Volume 26, March 2021
Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry, Volume 1, December 2019
Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry, Volume 5, December 2021
Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry, Volume 3, December 2020