Neuropharmacology, Volume 259, 15 November 2024
Brain Research, Volume 1843, 15 November 2024
Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Volume 333, 28 October 2024
Brain Research, Volume 1841, 15 October 2024
Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine, Volume 12, September 2024
Journal of Neuroscience Methods, Volume 409, September 2024
Brain Research, Volume 1838, 1 September 2024
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, Volume 14, July 2024
Neuropharmacology, Volume 252, 1 July 2024
Neuroscience Research, Volume 204, July 2024
Brain Research Bulletin, Volume 212, 15 June 2024
Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, Volume 129, June 2024
Journal of Neuroscience Methods, Volume 406, June 2024
Neurochemistry International, Volume 176, June 2024
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, Volume 219, June 2024
Brain Research, Volume 1832, June 2024
IBRO Neuroscience Reports, Volume 16, June 2024
Neuroscience, Volume 546, 14 May 2024
Journal of Ginseng Research, Volume 48, May 2024
Neuroscience, Volume 544, 19 April 2024
Brain Research, Volume 1829, 15 April 2024
Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, Volume 73, April 2024
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, Volume 217, February 2024
Neurobiology of Disease, Volume 190, January 2024
Experimental Gerontology, Volume 184, December 2023
Experimental Gerontology, Volume 183, November 2023
Translational Research in Anatomy, Volume 33, November 2023
European Journal of Radiology, Volume 165, August 2023
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, Volume 13, July 2023
Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine, Volume 7, June 2023
Neurochemistry International, Volume 165, May 2023
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, Volume 211, April 2023
Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, Volume 69, April 2023
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development, Volume 211, April 2023
Journal of Ginseng Research, Volume 47, March 2023
Experimental Neurology, Volume 360, February 2023
Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical, Volume 240, July 2022
Ageing Research Reviews, Volume 77, May 2022
Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 471, 5 August 2024
Neuroscience Letters, Volume 836, 27 July 2024
Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 465, 8 May 2024
Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 463, 12 April 2024
Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 456, 5 January 2024
Neuroscience Letters, Volume 810, 27 July 2023
Neuroscience Letters, Volume 803, 23 April 2023
Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, Volume 69, April 2023
Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 438, 13 February 2023
Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 437, 2 February 2023
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 15, August 2024
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, Volume 123, August 2024
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, Volume 123, August 2024
Journal of Nutrition, Volume 154, July 2024
Heliyon, Volume 10, 30 April 2024
Immunity, Volume 57, 9 April 2024
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 15, April 2024
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 119, April 2024
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 15, March 2024
Neurobiology of Stress, Volume 29, March 2024
Revista Espanola de Geriatria y Gerontologia, Volume 59, 1 January 2024
Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 7, November 2023
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, Volume 39, October 2023
Immunity, Volume 56, 12 September 2023
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 14, July 2023
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 117, June 2023
Journal of Nutrition, Volume 153, May 2023
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 117, March 2023
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 116, December 2022
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 116, 1 November 2022
Advances in Nutrition, Volume 13, 1 March 2022
Journal of Nutrition, Volume 152, 1 January 2022
Neurochemistry International, Volume 177, July 2024
Experimental Neurology, Volume 374, April 2024
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2024, ISSN 2211-3835
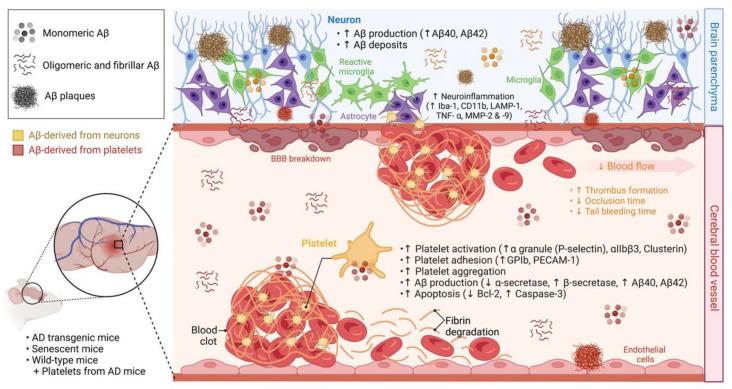
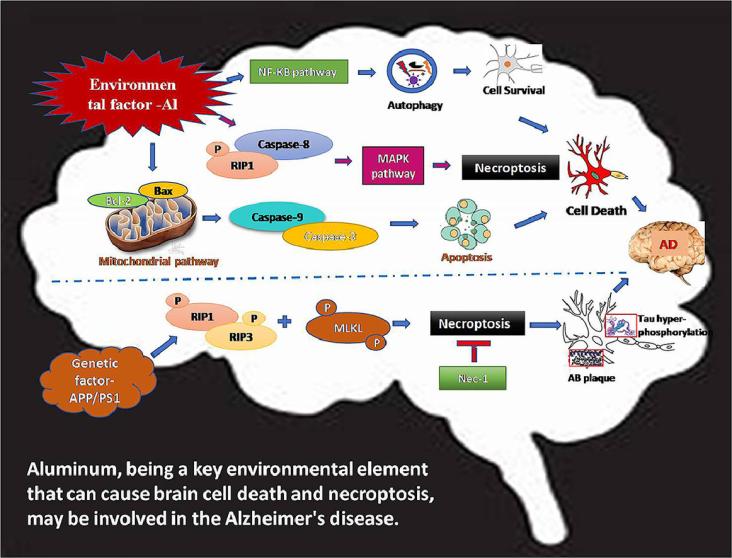
The study introduces a nano-modulator that targets the damaged blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. This modulator releases therapeutic agents that reduce amyloid-beta load, alleviate neuroinflammation, and restore neurovascular unit function, showing potential for Alzheimer’s treatment.
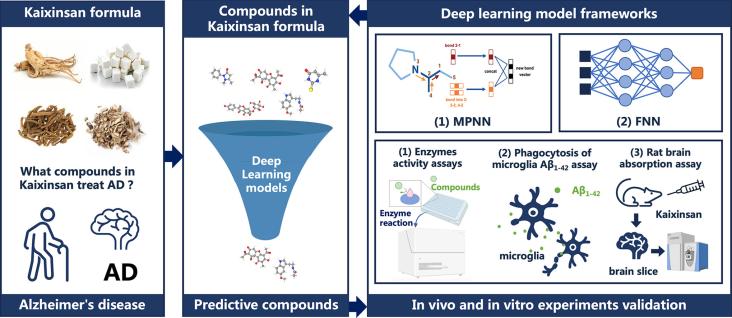
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2024, 101022, ISSN 2095-1779
This study developed four deep learning models to identify potential Alzheimer's disease treatments from traditional Chinese medicine, specifically the Kaixinsan formula. The models successfully predicted compounds that showed significant anti-Alzheimer's activities in various experimental validations.
The American Journal of Medicine, Available online 27 August 2024
The present mini-commentary on Alzheimer's disease describes recently revealed pathogenic elements, evolving capabilities for identifying unusually high individual susceptibility and developing tests that predict onset preclinically to allow preventative approaches. Several potential therapies that target cellular signaling and other pathways that are abnormal in Alzheimer's disease are in early clinical trials and will be reviewed briefly.