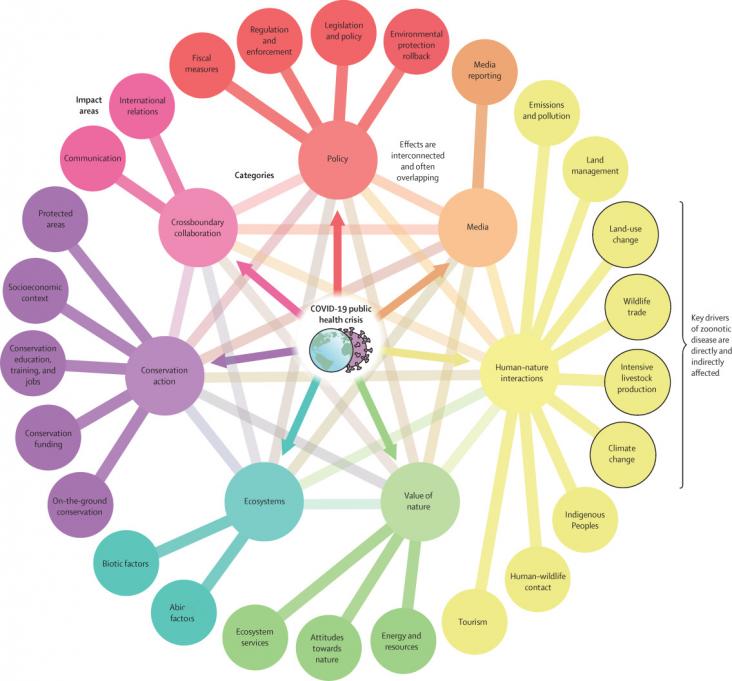
World Environment Day is the most renowned day for environmental action. Since 1974, it has been celebrated every year on June 5th, engaging governments, businesses, celebrities and citizens to focus their efforts on a pressing environmental issue.
To mark World Environment Day 2022, Elsevier presents a curated list of publicly available journal articles and book chapters in support of this year's theme - Only One Earth. This year, Sweden is hosting World Environment Day and marks the 50th anniversary of the first United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, held in Stockholm in 1972. “Only One Earth” was the slogan for the original Stockholm Conference. World Environment Day 2022 is re-energizing the slogan to emphasize that planet Earth is still the only liveable planet we have and to push for transformative actions to reset the balance between people and the natural world to create a better future for all.
Please share this impactful research because we have #OnlyOneEarth. Let's take care of it.
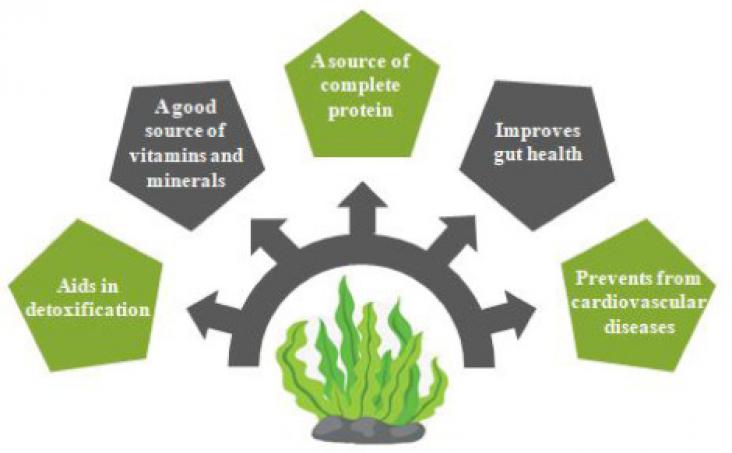
Future Foods, Volume 5, June 2022
The eminent protein sources among the vegetarian population include cereals and pulses that do not satisfy the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) level. The anti-nutrients such as protease inhibitors are responsible for the diminished bioavailability of plant protein. Consumption of a protein deficit diet severely impacts muscle health; hence, it becomes necessary to design an alternative source of complete protein. One such non-meat source with all essential amino acids in required quantity is seaweeds, an aquatic plant.
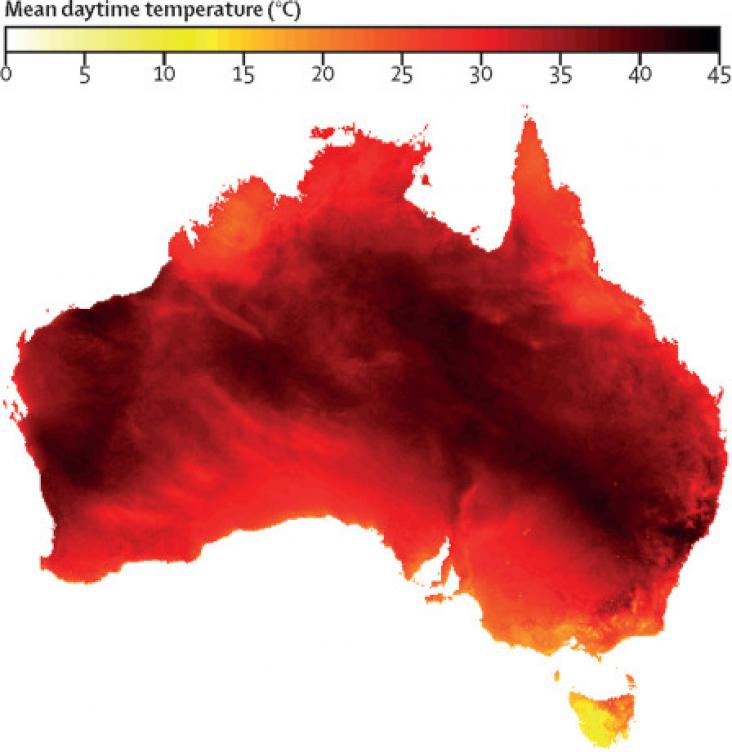
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 6, April 2022
Background: Increasing air conditioner use for cooling indoor spaces has the potential to be a primary driver of global greenhouse gas emissions. Moving indoor air with residential fans can raise the temperature threshold at which air conditioning needs to be turned on to maintain the thermal comfort of building occupants. We investigate whether fans can be used to reduce air conditioner use and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
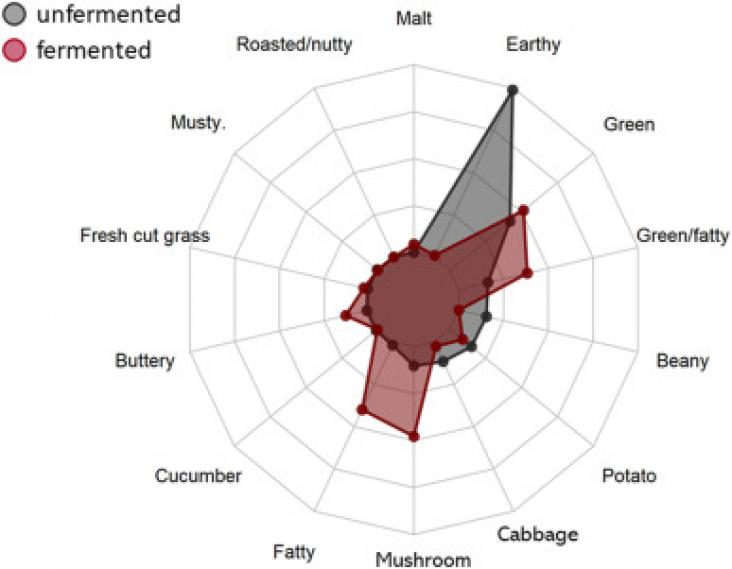
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 6, March 2022
Background: Numerous studies have quantified the associations between ambient temperature and enteric infections, particularly all-cause enteric infections. However, the temperature sensitivity of enteric infections might be pathogen dependent. Here, we sought to identify pathogen-specific associations between ambient temperature and enteric infections.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 6, February 2022
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 6, February 2022
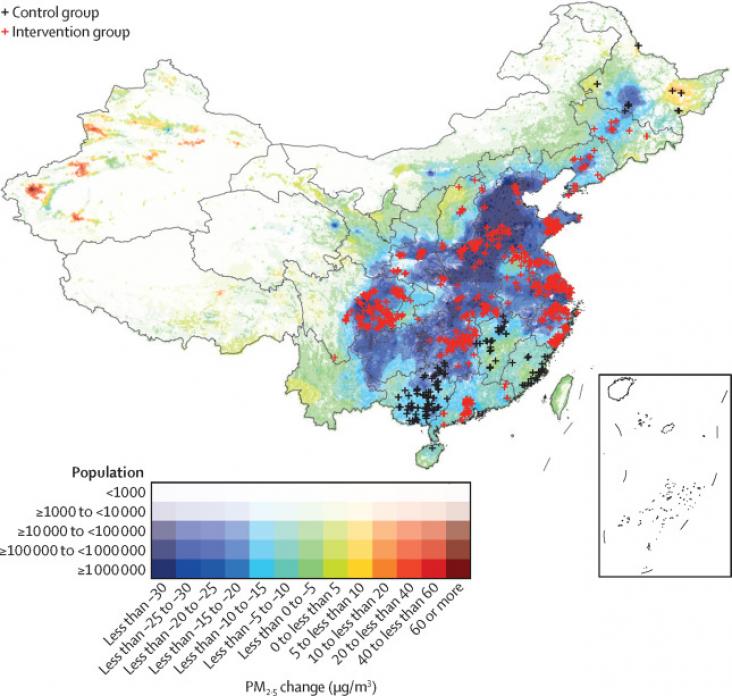
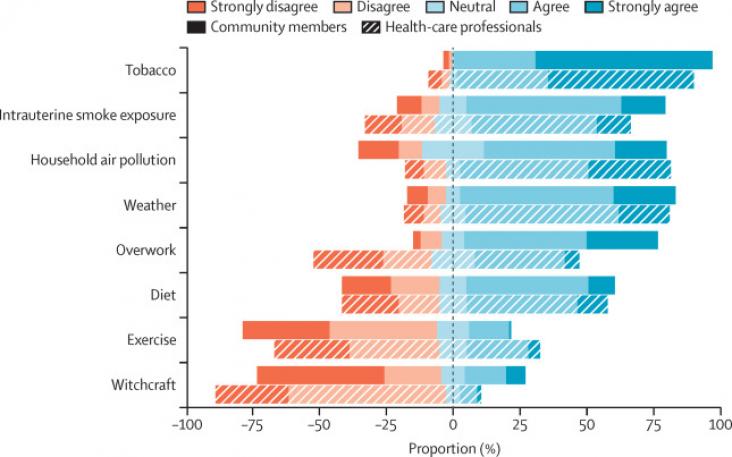
The Lancet Healthy Longevity, Volume 3, February 2022
Background: Air pollution might accelerate cognitive ageing; it is unclear whether large-scale interventions, such as China's Clean Air Act (CCAA), can mitigate cognitive deterioration. We aimed to evaluate the effect of CCAA on changes in cognitive function in older adults. Methods: In this population-based, quasi-experimental study, we did a difference-in-differences analysis of the data collected during the 2014 and 2018 waves of the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (CLHLS).
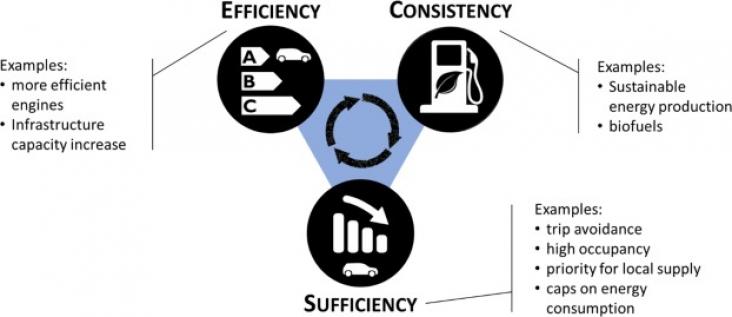
Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, Volume 103, February 2022
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, December 2021
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, December 2021
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, June 2021
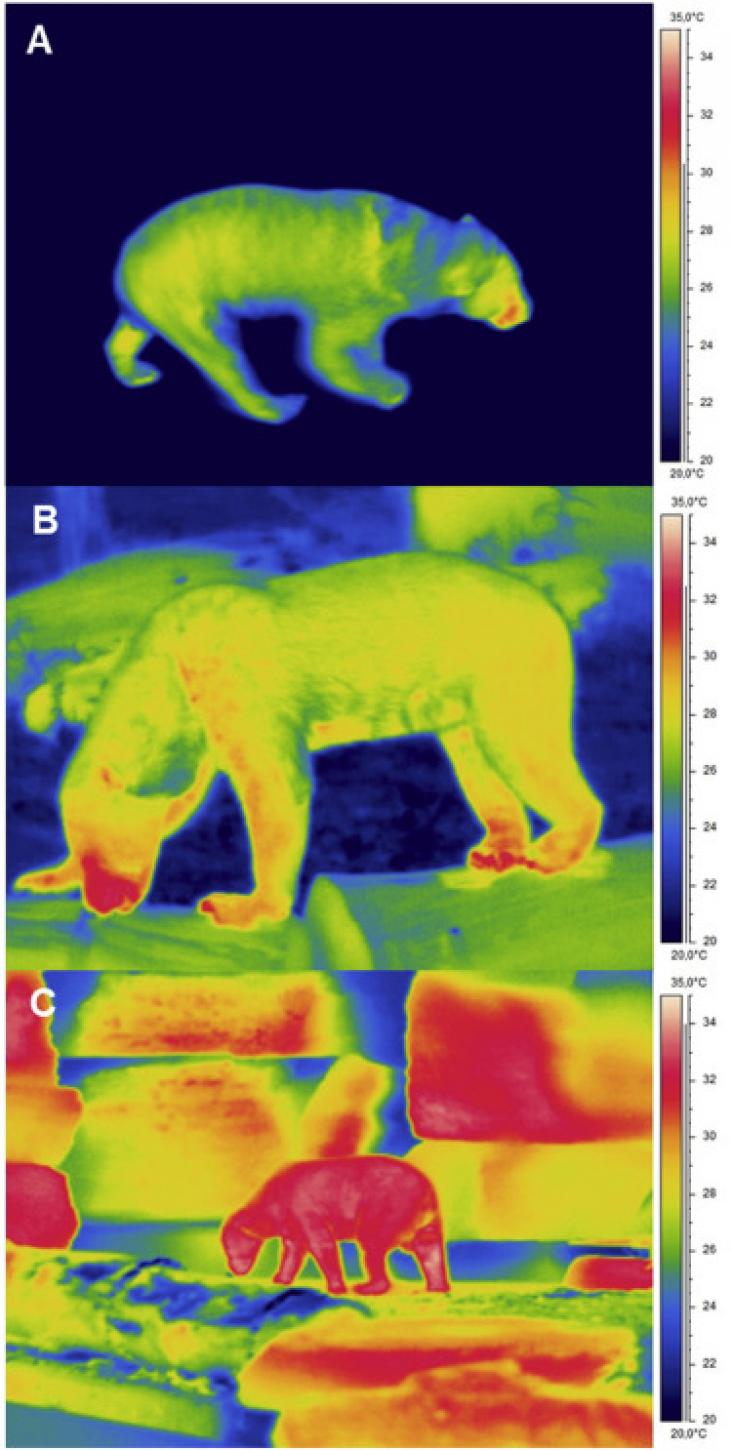
Temperature affects many life processes, but its effect might be expected to differ among eukaryotic organisms inhabiting similar environments. We reviewed literature on temperature thresholds of humans, livestock, poultry, agricultural crops, and sparse examples of fisheries. We found that preferable and harmful temperatures are similar for humans, cattle, pigs, poultry, fish, and agricultural crops. Preferable temperatures range from 17°C to 24°C. Stress temperature thresholds are lower when humidity is higher.
Journal of Thermal Biology, Volume 97, April 2021
Compared to other climate regions of the world, Mediterranean regions are likely to experience more severe effects of climate change as rainfall decreases and temperatures increase. Global climate change models predict a reduction in rainfall and rise in the temperature of rivers in South Africa's Cape Fold Ecoregion (CFE) – a Mediterranean region in the south-west corner of the country.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, March 2021
Climate change can have detrimental effects on child health and wellbeing. Despite the imperative for a fuller understanding of how climate change affects child health and wellbeing, a systematic approach and focus solely on children (aged <18 years) has been lacking. In this Scoping Review, we did a literature search on the impacts of climate change on child health from January, 2000, to June, 2019. The included studies explicitly linked an alteration of an exposure to a risk factor for child health to climate change or climate variability.
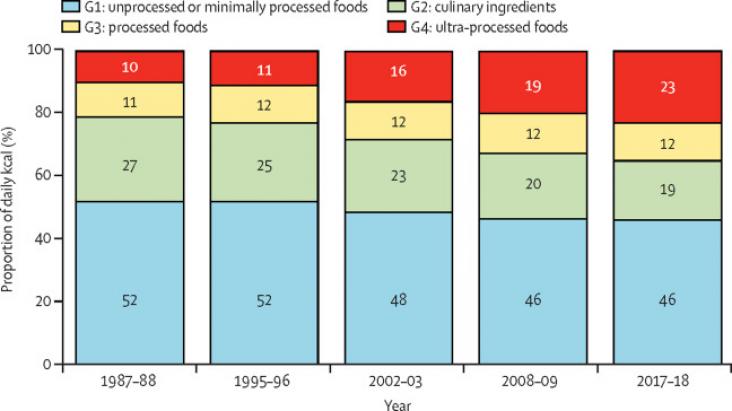
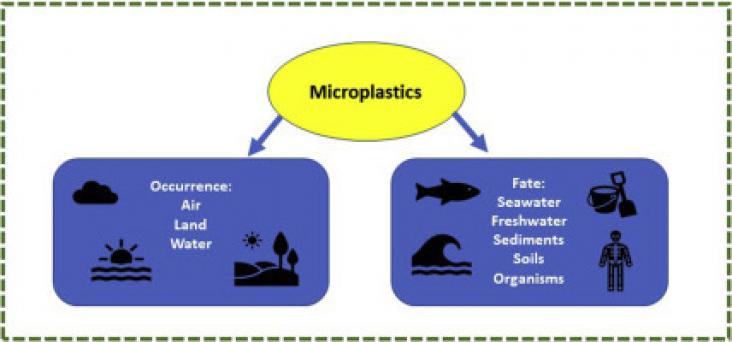
Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 32, December 2021
Microplastics (MPs) are found in all conceivable media from air, sediments, soils, freshwater, seawater, and organisms, including humans. This paper emphasizes current advances in the study of MPs and presents a review of recent two years of literature on the occurrence and fate of these particles in the environment. The occurrence and fate of MPs are affected by their characteristics and interaction with the media in the environment, including particle mobility and transport processes.
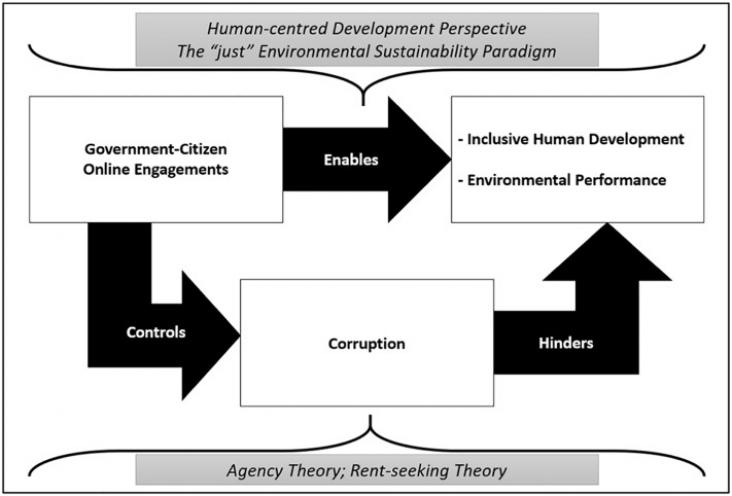
Digital Geography and Society, Volume 2, January 2021
These are uncertain times in the Anthropocene, where the health and resilience of all urban inhabitants should be key themes for cities striving for sustainability. To this end, local councils in Australia are applying digital technologies with increasing complexity as components of their urban forest management. This paper applies a more-than-human lens to analyse Australian local council urban forest policies, documents and project information for their inclusion and application of digital technologies.
Indigenous People and Nature, Insights for Social, Ecological, and Technological Sustainability, 2022, Pages 3-27
Modern Cartography Series, Volume 10, 2021, Pages 313-335
Modern Cartography Series, Volume 10, 2021, Pages 1-15
International Environmental Cooperation and The Global Sustainability Capital Framework, 2021, Pages 1-15
The Impacts of Climate Change, A Comprehensive Study of Physical, Biophysical, Social, and Political Issues, 2021, Pages 3-17
Contamination of Water, Health Risk Assessment and Treatment Strategies, 2021, Pages 99-107
Contamination of Water, Health Risk Assessment and Treatment Strategies, 2021, Pages 49-64
Contamination of Water, Health Risk Assessment and Treatment Strategies, 2021, Pages 265-284
Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology (Third Edition), 2022, Pages 833-843
Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals (Fifth Edition), Volume I: General Considerations, 2022, Pages 137-182
Endocrine Disruption and Human Health (Second Edition), 2022, Pages 485-498
Encyclopedia of Environmental Health (Second Edition), 2019, Pages 315-323
Encyclopedia of Environmental Health (Second Edition), 2019, Pages 436-455
Encyclopedia of Environmental Health (Second Edition), 2011, Pages 327-334
Encyclopedia of the World's Biomes, 2020, Pages 12-21
Encyclopedia of the World's Biomes, 2020, Pages 193-200