Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a major threat to human health around the world.
Background & aims: Recent experimental models and epidemiological studies suggest that specific environmental contaminants (ECs) contribute to the initiation and pathology of non-alcoholic fatty l
Problem: Within maternity care policies and practice, pregnant migrant women are regarded as a vulnerable population.
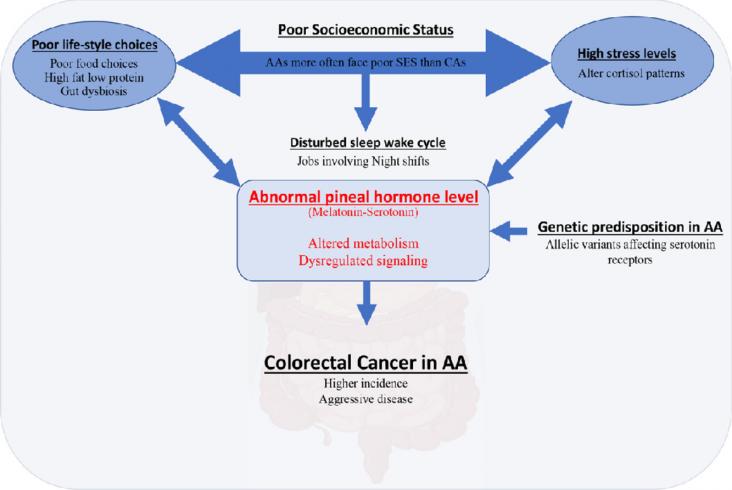
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States.
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 10 by assessing SARS-CoV-2 incidence in six ethnic groups in Amsterdam, and showing that incidence was highest in the largest minority ethnic groups. The findings suggest that prevention measures and vaccination should be especially encouraged in these groups.
Land use and land cover changes in the Jedeb and Chemoga watersheds have been detected in the past 29 years.
This Article supports SDG 3 by showing the association between unstable housing (the lack of access to adequate or fixed housing) with HIV and HCV infection among people who inject drugs, finding that a substantial proportion of infections (11.2% of new HCV infections in the study period) and suggesting that the broader social needs of this population, including housing, should be addressed as part of efforts to reduce and eliminate these infections.
The Comment, linked to the above Article on unstable housing, contributes to SDG 3 by calling for a 100-100-100 target: "stably housing 100% of PWID who are unstably housed, providing 100% of PWID access to consistent and adequate harm reduction services, and offering treatment to 100% of PWID who want substance use treatment". Such a target would be in important part of HIV and HCV elimination efforts.
This paper addresses pharmaceutical detection in groundwater.
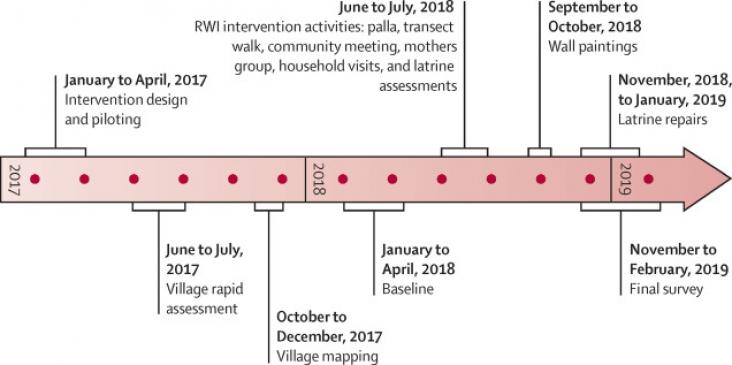
This study supports SDGs 3 and 6 by investigating a low-cost behavioural intervention designed to increase latrine use and safe disposal of child faeces in India. The study found the intervention modestly increased latrine use and markedly increased safe disposal of child faeces in the short term, but was unlikely to reduce exposure to pathogens to a level necessary to achieve health gains.
