This Review supports SDG 5 by describing a new framework and capacity development approach, the Public Leadership for Gender Equality (PL4GE), that promotes six key leadership practices for gender transformative change in public health.
This viewpoint supports SDGs 3, 5, 10 and 16, focusing on the drivers of Black maternal mortality and advocating the collection of disaggregated data to support improvements in Black maternal health.
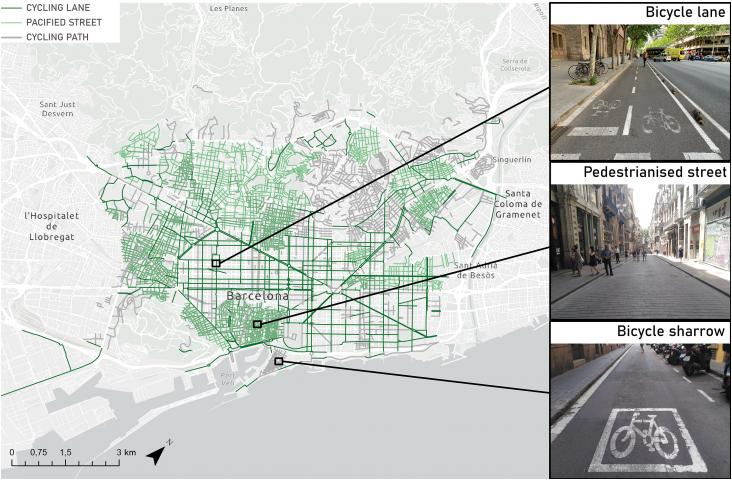
This Study supports SDG 5 and SDG 11 by discussing innovations in micro-mobility and their unequal impacts by gender.
In support of SDG 5 and 11, this Study discusses which transport infrastructure innovations are required to support gender-equitable cycling, especially in developing countries.
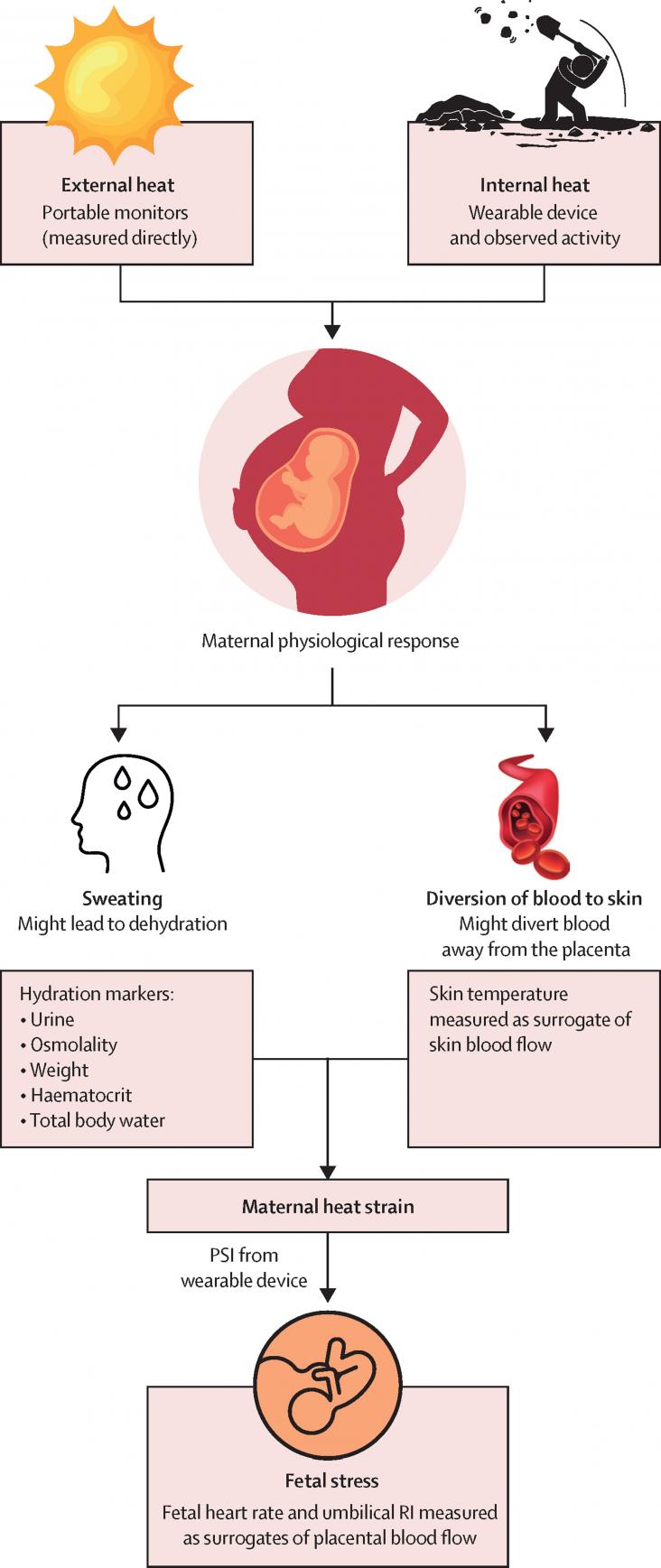
This Article supports SDGs 3, 5, and 13, focusing on the mechanisms for adverse outcomes caused by environmental heat stress in pregnant subsistence farmers.
This Study supports SDGs 3, 5 and 10 by exploring the national impact of limited English proficiency (LEP) in breast cancer screening. Previously unknown, the results showed that LEP women, particularly Spanish speakers, are associated with a lower probability of having a screening mammogram.
This chapter aligns with SDG Goal 5: Gender equality and Goal 9: Industry, innovation and infrastructure by exploring the role women have played in disaster recovery and how this engagement fosters and enhances women's leadership roles.
This Study supports SDGs 3, 5 and 10 by highlighting the significant variability in insurance coverage of Prophylactic Mastectomy (PM) between companies which can lead to further inequalities in access to this breast cancer risk reducing procedure. Physicians and patients alike should advocate for fair and equal access to PM for certain clinical indications.
This study is the largest international investigation of women's representation in internal medicine specialties, revealing that women constitute 35% of practicing physician specialists and 43% of trainees. It identifies cardiology, gastroenterology, and respiratory/critical care as the specialties with the most significant underrepresentation of women, highlighting the need for strategies to create a more diverse and representative workforce in these fields.
This Article supports SDGs 3, 5 and 10, summarizing a discussion on workplace flexibility held by the AAWR at the RSNA 2021 Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting, and highlighting the positive impact various aspects of flexible work arrangements have on women.
