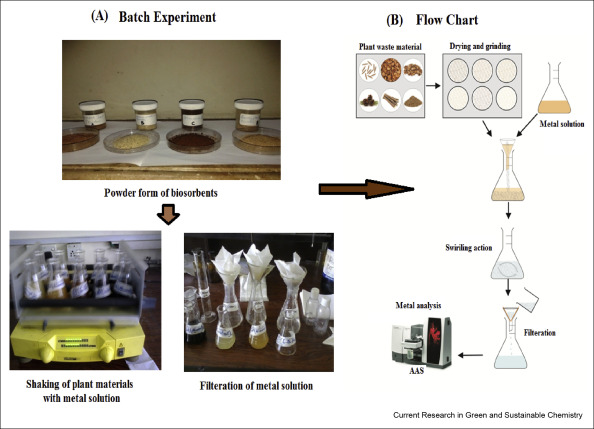
This research explores the use of indigenous waste plant materials for an easy and cost-effective approach for the removal of heavy metals from water.
This book chapter addresses SDGs 3 and 10 by explaining how stakeholders can ensure the most accurate data about food security for policymakers.
The SDG Impact of COVID-19 podcast series gathers expert opinion exploring the impact of COVID-19 on the Sustainable Development Goals. In this segment, we get the view of Monika Froehler, CEO of the Ban Ki-moon Centre for Global Citizens.
Elsevier,
Mental and Behavioral Health of Immigrants in the United States, Cultural, Environmental, and Structural Factors, 2020, Pages 157-178
This chapter advances SDGs 3 and 10 by exploring how to achieve a culturally competent practice while continuing efforts are needed across various race and ethnicities as well as age groups to provide a more holistic approach to mental health treatment as well as promote protective factors such as a positive cultural identity of immigrants in the United States and worldwide.
Elsevier,
Mental and Behavioral Health of Immigrants in the United States, Cultural, Environmental, and Structural Factors, 2020, Pages 219-252
This chapter advances SDGs 3 and 10 by addressing the prevalence of mental disorders among the ethnic minority groups (African American, Latinx, and Asian American) in the United States according to immigration status.
Alzheimer's disease may cause respiratory disorders. Levothyroxine can reduce lung inflammation and oxidative stress. Treatment with Levothyroxine may partially improve Alzheimer's disease.
This book chapter advances SDG 3 and 10 by providing information on various culturally sensitive methods to assess and treat mental health conditions onset by factors contributing to the immigration process for adolescents, adults, and older adults.
Findings from multiple studies link acculturation processes to the psychological and behavioral health of Latino immigrant population in the United States. A critical factor impacting this relation is the context of reception where immigrants settle. Several studies of acculturation have been conducted in traditional receiving contexts, and less attention has been paid to Latino immigrants in emerging contexts. In this chapter, we have discussed how traditional and emerging contexts of reception can confer very different experiences to Latino immigrants, and their significant implications for Latino immigrant health. Further, given the recent influx of crisis migrants from Central America, we have discussed receiving contexts for these newest Latino immigrants to the United States and demonstrated how such contexts might impact their psychological and behavioral health. We concluded with a discussion of implications for the development of policy, as well as culturally specific prevention and intervention programs for Latino immigrants.
Multidisciplinary analytical techniques allow us to examine the presence and behaviour of pollutants in complex atmospheric, terrestrial, aquatic, and living compartments of ecosystems. This book chapter advances SDGs 6, 13 and 15.
This book chapter advances SDG 3 and 6 by describing properties of water and importance of water to biomaterials and biology.