On April 22 every year, we celebrate the anniversary of the birth of the modern environmental movement with Earth Day. Since the first Earth Day in 1970, this day has marked global collaboration and awareness of the need to fight for a cleaner and healthier Earth. It all began in 1962 when Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring hit the New York’s bestseller list selling over 500,000 copies in 24 countries. As public awareness and concerns were raised over the environment, and the links between pollution and public health were put in the spotlight, Earth Day 1970 would come to provide a voice to this emerging environmental awareness. Today, with over 190 engaged and committed countries and over 1 billion individuals involved, Earth Day has come a long way. Since the first Earth Day, important strides have been made worldwide including the signing of the historic Paris Agreement and the implementation of the UN Sustainable Development Goals, and Earth Day continues to grow every year.
This year, the theme is “Invest In Our Planet” with a focus on preserving and protecting our health, our families, and our livelihoods because a green future is a prosperous future. To help you engage with Earth Day and its values, Elsevier presents a curated list of publicly available journal articles and book chapters. At Elsevier, we support environmental awareness an the goal of achieving a sustainable and equitable future. Together, we must #InvestInOurPlanet.
Telematics and Informatics, Volume 58, May 2021
We investigate the role of creative skilled migrants in broadcasting an alternative use of technology in support of a sustainable smart city. We do so by analyzing the themes they produced on Twitter. We focus on Amsterdam as a case, and urban planners and designers as examples of creative migrants. Computational methodology allowed for a selection of naturally occurring data in social media.
Habitat International, Volume 115, September 2021
Tracking progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) requires monitoring of various social-ecological indicators over space and time, including the ratio of land consumption rate to population growth rate (LCRPGR), an indicator of land-use efficiency (SDG 11.3.1). In this study, we analyzed state-of-the-art Earth observation data (1975–2015) to address three key questions. First, how has the LCRPGR varied over space and time? Second, how is built-up expansion related to population increase across regions?
Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, Volume 103, February 2022
Transportation is a basic social need, but most trips are done by private vehicles, which is not environmentally sustainable with growing urban populations. Micromobility (e.g., shared bikes) represents a significant opportunity to replace short private vehicles trips (0–3 miles) and reduce transportation sector emissions. This paper uses Seattle as a case study and estimates that up to 18% of short car trips could be replaced by micromobility.
Chest, Volume 161, March 2022
Background: Individuals with COPD have increased sensitivity to traffic-related air pollution (TRAP) such as diesel exhaust (DE), but little is known about the acute effects of TRAP on exercise responses in COPD. Research Question: Does exposure before exercise to TRAP (DE titrated to 300 μg/m3 particulate matter < 2.5 μm in diameter [DE300]) show greater adverse effects on exercise endurance, exertional dyspnea, and cardiorespiratory responses to exercise in participants with mild to moderate COPD compared with former smokers with normal spirometry and healthy control participants?
Future Foods, Volume 5, June 2022
Meat induces large environmental impact while supplying important nutrients, and meat substitutes are increasingly adopted as direct replacers of meat products. This study assessed the environmental impact of a pork schnitzel and two soy-based schnitzels in terms of three different functional units to reflect the products’ functions as meal components and suppliers of high quality proteins. For a functional unit of 1 kg of product, the pork schnitzel induces the largest environmental impact for most environmental impact indicators.
Chest, Volume 160, November 2021
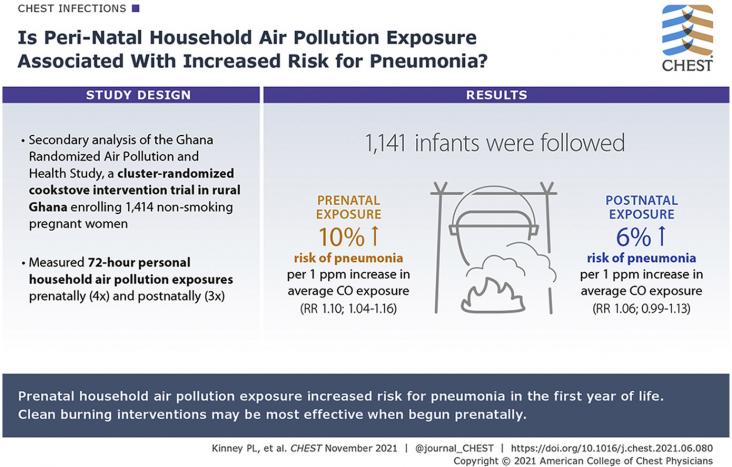
Background: Nearly 40% of the world's population is exposed daily to household air pollution. The relative impact of prenatal and postnatal household air pollution exposure on early childhood pneumonia, a leading cause of mortality, is unknown. Research Question: Are prenatal or postnatal household air pollution, or both, associated with pneumonia risk in the first year of life? Study Design and Methods: The Ghana Randomized Air Pollution and Health Study enrolled 1,414 nonsmoking, pregnant women before 24 weeks’ gestation with prospective follow-up to the child's age of 1 year.
Habitat International, Volume 117, November 2021
Ethiopia has experienced rapid urbanization over the past three decades. Several cities expanded rapidly and many satellite towns sprung up around the major cities. The high rate of urbanization and urban growth resulted in high demand for urban land, mainly for industrial, commercial, and residential purposes. In order to meet the demand, an enormous amount of land has been made available for urban use, mainly through land conversion. However, we know very little about how efficiently cities use urban land.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, November 2021
Background: The announcement of China's 2060 carbon neutrality goal has drawn the world's attention to the specific technology pathway needed to achieve this pledge. We aimed to evaluate the health co-benefits of carbon neutrality under different technology pathways, which could help China to achieve the carbon neutrality goal, air quality goal, and Healthy China goal in a synergetic manner that includes health in the decision-making process.
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 6, November 2021
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, July 2021
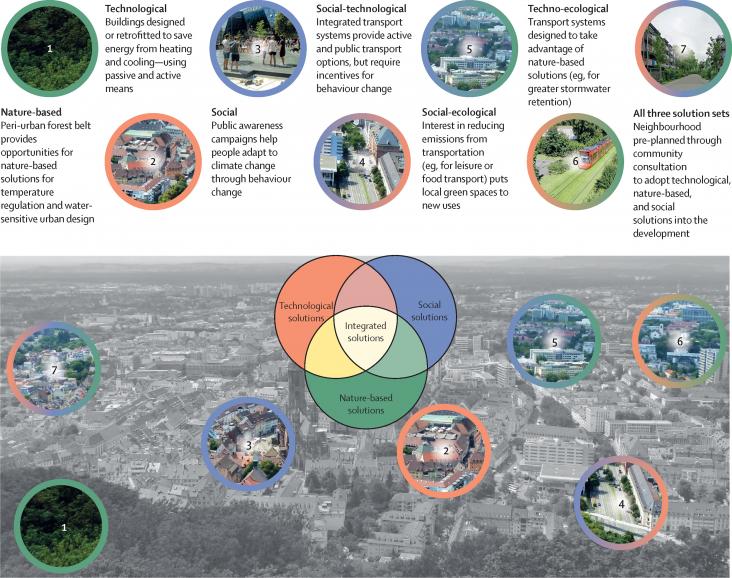
Record climate extremes are reducing urban liveability, compounding inequality, and threatening infrastructure. Adaptation measures that integrate technological, nature-based, and social solutions can provide multiple co-benefits to address complex socioecological issues in cities while increasing resilience to potential impacts. However, there remain many challenges to developing and implementing integrated solutions.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, June 2021
Background: Extreme heat exposure can lead to premature death. Climate change is expected to increase the frequency, intensity, and duration of extreme heat events, resulting in many additional heat-related deaths globally, as well as changing the nature of extreme cold events. At the same time, vulnerability to extreme heat has decreased over time, probably due to a combination of physiological, behavioural, infrastructural, and technological adaptations. We aimed to account for these changes in vulnerability and avoid overstated projections for temperature-related mortality.
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 8, August 2020
Environmental Systems Science, Theory and Practical Applications, 2021, Pages 509-542
Preparing a Workforce for the New Blue Economy, People, Products and Policies, 2021, Pages 3-16
Modern Cartography Series, Volume 10, 2021, Pages 313-335
Climate Change and Crop Stress, Molecules to Ecosystems, 2022, Pages 209-229
Climate Change Science, Causes, Effects and Solutions for Global Warming, 2021, Pages 223-246
Sustainable Resource Management, Modern Approaches and Contexts, 2021, Pages 289-315
Environmental Sustainability and Economy, 2021, Pages 35-60
Methods in Sustainability Science, Assessment, Prioritization, Improvement, Design and Optimization, 2021, Pages 13-26
Ethnozoology, Animals in Our Lives, 2018, Pages 119-149
Animals and Human Society, 2018, Pages 451-482
Marine Mammal Ecotoxicology, Impacts of Multiple Stressors on Population Health, 2018, Pages 291-320
The Atlantic Walrus, Multidisciplinary insights into human-animal interactions, 2021, Pages 251-262
Animal Behavior (Third Edition), 2022, Pages 531-573
Galapagos Giant Tortoises, Biodiversity of World: Conservation from Genes to Landscapes, 2021, Pages 503-509
Climate Change Adaptation for Transportation Systems, 2021, Pages 1-24
Disaster Resilience and Sustainability, Adaptation for Sustainable Development, 2021, Pages 1-20
Improving Sustainable Viticulture and Winemaking Practices, 2022, Pages 1-24
Agriculture's Ethical Horizon (Third Edition), 2022, Pages 1-15
Social Ecology in the Digital Age, Solving Complex Problems in a Globalized World, 2018, Pages 223-264
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, November 2021
Background: The announcement of China's 2060 carbon neutrality goal has drawn the world's attention to the specific technology pathway needed to achieve this pledge. We aimed to evaluate the health co-benefits of carbon neutrality under different technology pathways, which could help China to achieve the carbon neutrality goal, air quality goal, and Healthy China goal in a synergetic manner that includes health in the decision-making process.
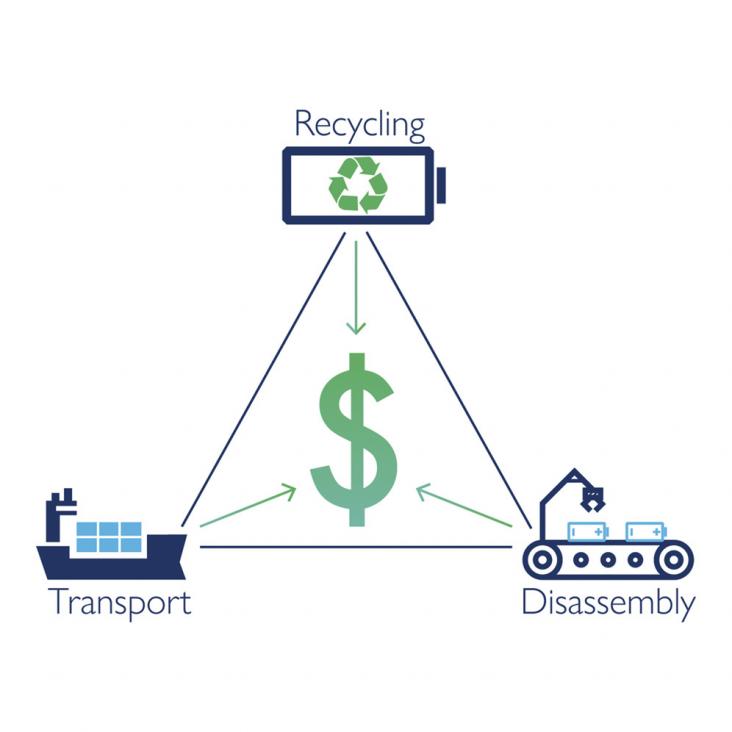
iScience, Volume 24, 23 July 2021
Economically viable electric vehicle lithium-ion battery recycling is increasingly needed; however routes to profitability are still unclear. We present a comprehensive, holistic techno-economic model as a framework to directly compare recycling locations and processes, providing a key tool for recycling cost optimization in an international battery recycling economy. We show that recycling can be economically viable, with cost/profit ranging from (−21.43 - +21.91) $·kWh−1 but strongly depends on transport distances, wages, pack design and recycling method.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, July 2021
Record climate extremes are reducing urban liveability, compounding inequality, and threatening infrastructure. Adaptation measures that integrate technological, nature-based, and social solutions can provide multiple co-benefits to address complex socioecological issues in cities while increasing resilience to potential impacts. However, there remain many challenges to developing and implementing integrated solutions.
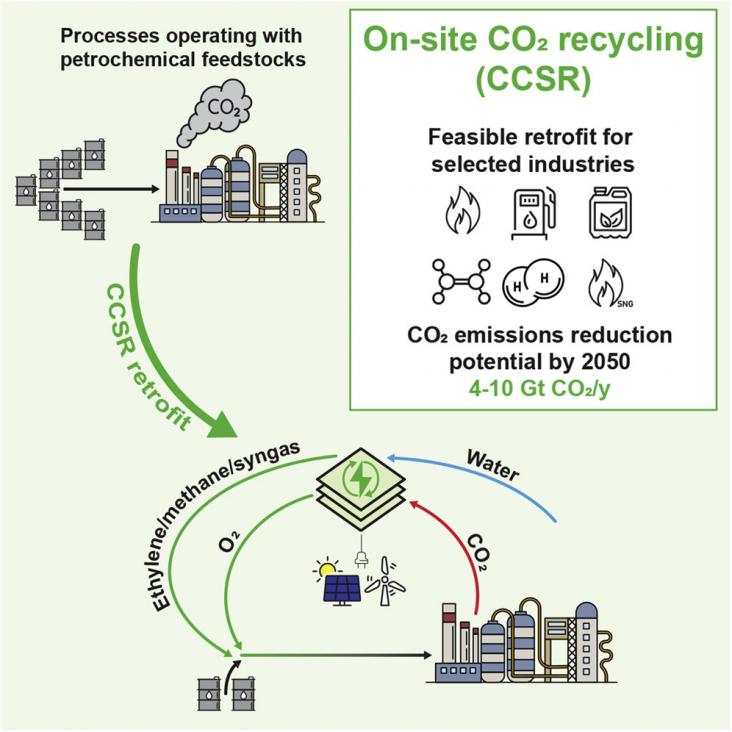
iScience, Volume 24, 25 June 2021
The chemical industry needs to significantly decrease carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in order to meet the 2050 carbon neutrality goal. Utilization of CO2 as a chemical feedstock for bulk products is a promising way to mitigate industrial emissions; however, CO2-based manufacturing is currently not competitive with the established petrochemical methods and its deployment requires creation of a new value chain.
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, June 2021
Background: Extreme heat exposure can lead to premature death. Climate change is expected to increase the frequency, intensity, and duration of extreme heat events, resulting in many additional heat-related deaths globally, as well as changing the nature of extreme cold events. At the same time, vulnerability to extreme heat has decreased over time, probably due to a combination of physiological, behavioural, infrastructural, and technological adaptations. We aimed to account for these changes in vulnerability and avoid overstated projections for temperature-related mortality.
iScience, Volume 24, 19 March 2021
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 8, August 2020
iScience, Volume 24, Issue 3, 2021, 102237