World Food Day is organized every year on October 16 to bring awareness to how our changing planet affects food production and distribution. In support of this year's theme "Our actions are our future- Better production, better nutrition, a better environment and a better life", Elsevier presents a collection of over 70 pieces of curated and freely available books and journal content.
Food Chemistry, Volume 364, 1 December 2021
Plant-based meat analogs are likely to have different gastrointestinal fates than real meat products due to differences in their compositions and structures. Here, we compared the gastrointestinal fate of ground beef and ground beef analogs using the INFOGEST in vitro digestion model, focusing on differences in microstructure, physicochemical properties, lipid digestion, and protein digestion in different regions of the model gut.
Food Quality and Preference, Volume 94, December 2021
Using data from Eurobarometer 83.4, this study combines the two branches of research that address climate-related and biodiversity-related opinions and actions of individuals in the EU. The literature shows that the differences between climate-related and biodiversity-related policies correspond, at an individual level, to a person's basic attitudes towards environmental protection and towards nature protection, respectively.
Food Quality and Preference, Volume 93, October 2021
In view of all kinds of sustainability concerns related to our current diet, it is essential to gain a good understanding of the sustainability motives consumers have for selecting their food. A comprehensive and validated scale to measure sustainability motives within the full range of food choice motives could contribute to this understanding, especially as sustainability is a multi-faceted concept in which the different aspects can sometimes be conflicting.
Food Chemistry, Volume 343, 1 May 2021
Food packaging can be considered as a passive barrier that protects food from environmental factors such as ultraviolet light, oxygen, water vapour, pressure and heat. It also prolongs the shelf-life of food by protecting from chemical and microbiological contaminants and enables foods to be transported and stored safely. Active packaging (AP) provides the opportunity for interaction between the external environment and food, resulting in extended shelf-life of food. Chemoactive packaging has an impact on the chemical composition of the food product.
Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, Volume 62, June 2020
Chitin is the structural material of crustaceans, insects, and fungi, and is the second most abundant biopolymer after cellulose on earth. Chitosan, a deacetylated derivative of chitin, can be obtained by deacetylation of chitin. It is a functionally versatile biopolymer due to the presence of amino groups responsible for the various properties of the polymer. Although it has been used for various industrial applications, the recent one is its use as a biodegradable antimicrobial food packaging material.
Current Opinion in Food Science, Volume 30, December 2019
Enteric viruses are an important food safety concern and have been associated with many foodborne disease outbreaks. Norovirus and Hepatitis A virus have been implicated in majority of outbreaks; however, other foodborne viruses such as Hepatitis E virus, Sapovirus and Rotavirus can also present a risk to humans. Viral foodborne disease outbreaks have typically been associated with foods served raw including shellfish, fruits and vegetables. The contamination of food by viruses can occur anywhere in the supply chain.
Journal of Cereal Science, Volume 59, May 2014
All crops require nitrogen (N) for the production of a photosynthetically active canopy, whose functionality will strongly influence yield. Cereal crops also require N for storage proteins in the grain, an important quality attribute. Optimal efficiency is achieved by the controlled remobilization of canopy-N to the developing grain during crop maturation. Whilst N will always be required for crop production, targeting efficient capture and use will optimise consumption of this valuable macronutrient.
One Earth, Volume 4, 21 May 2021
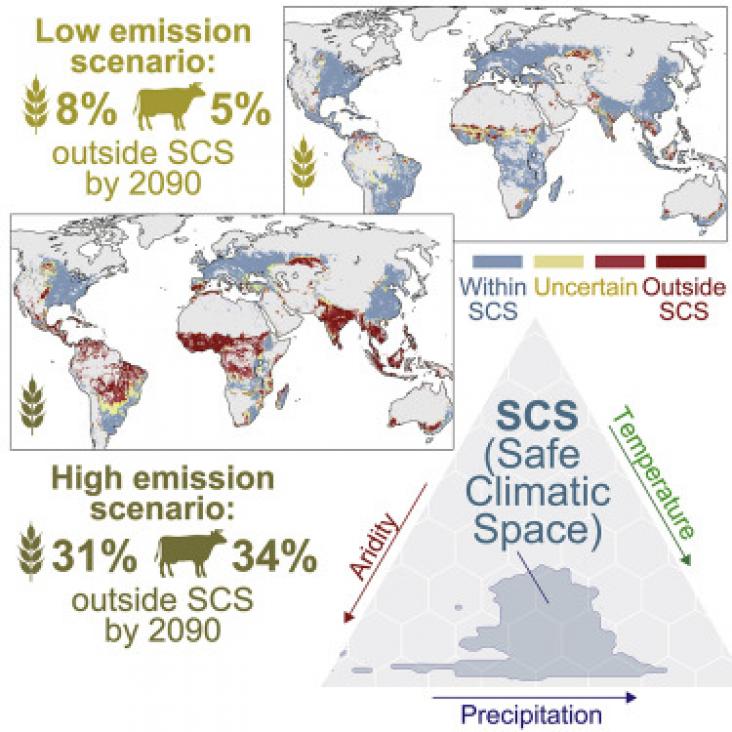
Food production on our planet is dominantly based on agricultural practices developed during stable Holocene climatic conditions. Although it is widely accepted that climate change perturbs these conditions, no systematic understanding exists on where and how the major risks for entering unprecedented conditions may occur. Here, we address this gap by introducing the concept of safe climatic space (SCS), which incorporates the decisive climatic factors of agricultural production: precipitation, temperature, and aridity.
Future Foods, Volume 4, December 2021
The global market for plant-based foods intended as alternatives to cheese products is increasing and will reach almost $4 billion by 2024. In this study, an evaluation of the composition, structure and physicochemical properties of four commercial plant-based block-style products was conducted, with results compared with those for Cheddar and processed cheeses. The plant-based products had considerably lower protein contents (0.11–3.00%) compared to the Cheddar and processed cheeses (25.04 and 18.50%, respectively).
Future Foods, Volume 4, December 2021
Substitution of beef with alternative proteins is one practical trend taken by industry and consumers to reduce the negative impact of convenience products on the environment. Numerous products based on plant, insect and fungi proteins compete to replace beef burgers in an environmentally friendly and healthy way. At the same time, there is a lack of studies which assess different options from environmental impact perspective but also with consideration of production scales, recipes, nutritional values, and sensory properties.
Saving Food: Production, Supply Chain, Food Waste and Food Consumption, Volume , 1 January 2019
Food waste is a great problem nowadays; while many people are starving around the world, tons of food is wasted every day. An efficient way to preserve food is using industrial processes such as heat, cold, drying, fermentation, irradiation, high pressure, pulsed electric fields and modified atmosphere, among others, but it is also possible to use active packaging (AP) to extend the shelf life of food products. This packaging uses active compounds, as antimicrobial and antioxidants that could be released over time in the food and its products and increase their shelf life.
Food and Society, 2020, Pages 247-255
Environmentalism and sustainability are two buzzwords that have come to represent an awakening of the people's collective conscience over the last two decades or so. Pedantically, the two words have slightly different meanings, yet there is sufficient overlap that they are commonly used interchangeably.
Climate Change and Food Security with Emphasis on Wheat, 2020, Pages 1-29